
- Home
- Trend
- Weight Loss Strategies
- Acne Tips
- Hair Health Information
- Blemish Removal Tips
- Acne Scar Removal Tips
- Muscle Building Techniques
- Intimate Care Tips
- Postpartum Intimate Care
- Eye Bags Wiki
- Tips for Face Slimming
- Secret of Permanent Hair Removal
- Breast Enlargement Tips
- Cure to Snoring
- Marionette Lines
- Skin-Tightening Secrets
Sunspots, also known as solar lentigines, are often confused with freckles. While both are common types of pigmentation, are triggered by UV exposure, and tend to appear on the cheeks, they are not the same. Regardless of the type, no one welcomes the appearance of these pesky spots. But if you want to prevent or eliminate them, the first step is to identify exactly what kind of pigmentation you're dealing with. In this article, we’ll teach you how to quickly distinguish between the five most common pigmentation types, share practical sun protection tips, and explore effective ways to treat sunspots.
What Are Sunspots (Solar Lentigines)?

Features of Sunspots
Sunspots (or solar lentigines) are pigmentation marks caused by UV exposure. They appear on the epidermis, usually flat, smooth, and brown in color. Their size varies from tiny like sesame seeds to as large as a coin. Typically round or oval, they are most commonly found on sun-exposed areas of the face such as the cheekbones, nose, cheeks, forehead, and outer eye corners. Fair-skinned individuals, middle-aged adults, and the elderly are more prone to sunspots.
Causes: UV Rays Are the Main Culprit
It’s widely known that UV rays in sunlight accelerate skin aging, making them the root cause of many skin problems — sunspots included. When skin is exposed to UV light, it produces melanin to protect underlying cells. The more UV exposure, the more melanin your skin will produce, especially without adequate sun protection. Over time, melanin accumulates and forms visible sunspots on the skin’s surface.
Why Do I Get Sunspots Without Sun Exposure?
You might wonder: if sunspots are caused by UV rays, why do they appear even when I don’t go out much? The answer: UV radiation isn’t exclusive to the sun. It’s also emitted from screens — mobile phones, tablets, and computers — which can also trigger melanin production and result in sunspots.
Besides UV rays, other contributing factors include genetics and individual constitution. Some people are simply more prone to pigmentation and may even develop visible spots as early as adolescence. Diet and lifestyle also play a role: picky eating, extreme dieting, sleep deprivation, and late nights can all accelerate the formation of sunspots.
How to Identify 5 Common Types of Pigmentation
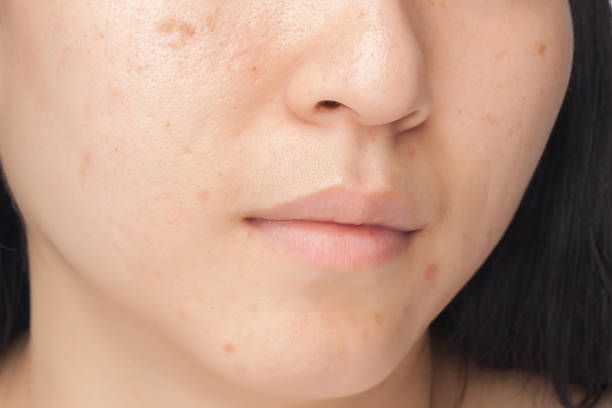
Are sunspots the same as freckles? Many people confuse sunspots with freckles. While both are pigmentation issues triggered by UV light, they differ in origin and appearance. Here’s how to distinguish between sunspots, freckles, and three other common pigmentation types:
1. Sunspots (Solar Lentigines)
• Appearance: Brown, round or oval, larger in size but variable (sesame seed to coin-sized), usually appear alone.
• Location: Forehead, cheeks, cheekbones — sun-exposed areas.
• Depth: Epidermal.
• Cause: Cumulative UV damage, especially without sunscreen, typically appears in middle age.
2. Freckles
• Appearance: Reddish or light brown, small (1–2 mm), irregular shape but uniform in size.
• Location: Cheeks, nose, neck, back of hands.
• Depth: Superficial.
• Cause: Primarily genetic, though UV exposure darkens them; often appear in childhood.
3. Hormonal Pigmentation (Melasma/Chloasma)
• Appearance: Light to dark brown, large, patchy, net-like pattern, symmetrical, blurred edges.
• Location: Face, especially sun-exposed areas.
• Depth: Deeper pigmentation.
• Cause: Hormonal changes (pregnancy, menopause, birth control), with UV and genetics as secondary factors.
4. Café-au-lait Spots
• Appearance: Light brown like “coffee with milk,” smooth edges, irregular shape, can appear anywhere on the body, size ranges from a few mm to 20 cm.
• Cause: Not UV-related; a type of birthmark caused by genetic conditions, often present from birth or early childhood.
5. Age Spots
• Appearance: Light to dark brown, often bean-sized or larger, raised and rougher with age.
• Location: Sun-exposed areas like face, hands, arms, neck.
• Depth: Deeper pigmentation.
• Cause: Skin aging, thickened keratin layer, and prolonged UV exposure; typically appears after age 40–50.
免費體驗
PicoCure Pigmentation Removal Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
How to Prevent Sunspots
Sunscreen is Non-Negotiable
Since UV rays are the leading cause of sunspots, sun protection is key. Sunscreen is an essential daily product — here’s how to choose the right one:
Choosing Sunscreen: SPF & PA Ratings
• SPF (Sun Protection Factor): Protects against UVB, starts at SPF15.
• PA (Protection Grade of UVA):
○ PA+: 2–4 hours
○ PA++: 4–8 hours
○ PA+++: 8+ hours
○ PA++++: up to 16 hours
Higher SPF and PA mean better protection — but also more burden on skin. Choose based on your needs:
• Indoor or short outings: SPF15–30, PA+ to PA++ is sufficient.
• Outdoor or prolonged sun: SPF50 and PA+++ or higher recommended.
Chemical vs Physical Sunscreen
• Chemical: Absorbs UV and converts it to heat. Lightweight and effective, but may irritate sensitive skin. Best for oily/combination skin.
• Physical: Reflects UV light. Gentler, good for sensitive or dry skin and children, but thicker and may leave a white cast.
Some modern sunscreens combine both types for balanced protection.
Tips for Proper Use
1. Apply sunscreen after skincare, before makeup.
2. Primer/BB cream isn’t a substitute — they don’t offer the same protection.
3. Use the right amount: 5ml (two-dollar coin size) for face, 35ml for full body.
4. Reapply every 2 hours, especially when sweating.
5. Cleanse thoroughly to avoid clogged pores and acne.
Natural Remedies: TCM-Inspired Anti-Spot Diet
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) believes pigmentation reflects internal imbalances in organs. Healing from within through diet can help improve skin tone over time.
Foods that May Help Reduce Sunspots:
White Fungus (Tremella)
Nourishes lungs and skin, rich in natural collagen-like substances that promote hydration and may reduce dark spots.
Tomatoes
High in vitamin C and lycopene; both help reduce melanin production and promote radiant skin.
Kiwifruit
Packed with fiber and vitamin C — helps brighten skin and delay pigmentation.
Strawberries
Rich in antioxidants and vitamin C — may help inhibit melanin and lighten spots.
Job’s Tears (Coix Seed)
Known for skin-brightening and anti-inflammatory effects; drinking coix seed water daily may improve skin tone and reduce spots.
How to Treat Sunspots?
Though harmless, sunspots can still affect appearance. Beyond dietary approaches, here are three common treatments:
1. Topical Creams
Dermatologists may prescribe creams with hydroquinone or tretinoin (Retin-A) to suppress melanin. These require long-term use and must be used under medical guidance to avoid irritation.
2. IPL (Intense Pulsed Light)
Early on, IPL was a popular option. It uses broad-spectrum light to target pigmentation and can also improve capillaries and fine lines. However, since it lacks precision and delivers diffuse heat, risks like burns or blisters exist — especially in untrained hands.
3. Laser Treatment
Unlike IPL, lasers use specific wavelengths to precisely break down pigment deep in the skin. Lasers act faster, are safer, and more targeted.
免費體驗
PicoCure Pigmentation Removal Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
The Gold Standard in Laser Spot Removal: Perfect Medical PicoCure™ Laser
Perfect Medical’s PicoCure Pigmentation Removal Treatment combines picosecond and nanosecond laser technologies — delivering energy 1,000x faster than traditional lasers. Its four wavelengths (1064nm, 650nm, 585nm, 532nm) reach deep into the dermis, breaking down stubborn pigmentation at different depths.
• Nanosecond laser breaks up pigment clusters.
• Picosecond laser pulverizes pigment into ultra-fine particles, which are naturally eliminated through metabolism.
Bonus: The laser also stimulates collagen production, helping to reduce wrinkles, refine pores, and brighten the skin. With FDA and CE certification, the PicoCure™ laser is non-invasive, painless, and has minimal risk of hyperpigmentation or scarring.
Want to try it? Click the link to register online and enjoy a trial session of Perfect Medical’s PicoCure Pigmentation Removal Treatment.
Register Your Session: Perfect Medical PicoCure Pigmentation Removal Treatment免費體驗
PicoCure Pigmentation Removal Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
FAQ

How are sunspots different from freckles and melasma?
Sunspots are larger, brown, and isolated — caused by cumulative sun exposure. Freckles are smaller, lighter, and often genetic. Melasma (hormonal spots) appear as patchy, blurry-edged pigmentation, usually caused by hormonal changes.
Can eating white fungus remove sunspots?
While white fungus has skin-nourishing properties and may brighten complexion, it cannot remove deep pigmentation. It helps support skin health over time, but expectations should be realistic.
Can I use lemon to lighten sunspots?
Be careful — lemon contains psoralen, a light-sensitive compound. Applying lemon then exposing your skin to UV can worsen pigmentation. It’s also acidic and may irritate skin.
How can I prevent sunspots?
The only real way is to block UV exposure through sun protection: hats, clothing, umbrellas, and sunscreen with appropriate SPF and PA. Follow proper sunscreen use guidelines for best results.
Is PicoCure™ laser effective for sunspots?
Absolutely. With advanced dual-wave laser and deep-skin penetration, it breaks down melanin precisely and stimulates collagen. Suitable for all types of pigmentation including sunspots, freckles, and melasma. Try a session through Perfect Medical’s free trial offer.








