
- Home
- Trend
- Weight Loss Strategies
- Acne Tips
- Hair Health Information
- Blemish Removal Tips
- Acne Scar Removal Tips
- Muscle Building Techniques
- Intimate Care Tips
- Postpartum Intimate Care
- Eye Bags Wiki
- Tips for Face Slimming
- Secret of Permanent Hair Removal
- Breast Enlargement Tips
- Cure to Snoring
- Marionette Lines
- Skin-Tightening Secrets
Skin rashes can be stubborn and difficult to cure. Often chronic in nature, they appear as dense clusters of red spots on various areas of the body, sometimes accompanied by itching or oozing. The causes of skin rashes are wide-ranging and can be triggered by both external environmental factors and internal hormonal imbalances. In this post, we’ll break down the 6 most common types of skin rashes and offer expert-backed treatment options to help you overcome them. Don’t miss the recommended skin-renewing solution at the end!
What Is A Skin Rash?
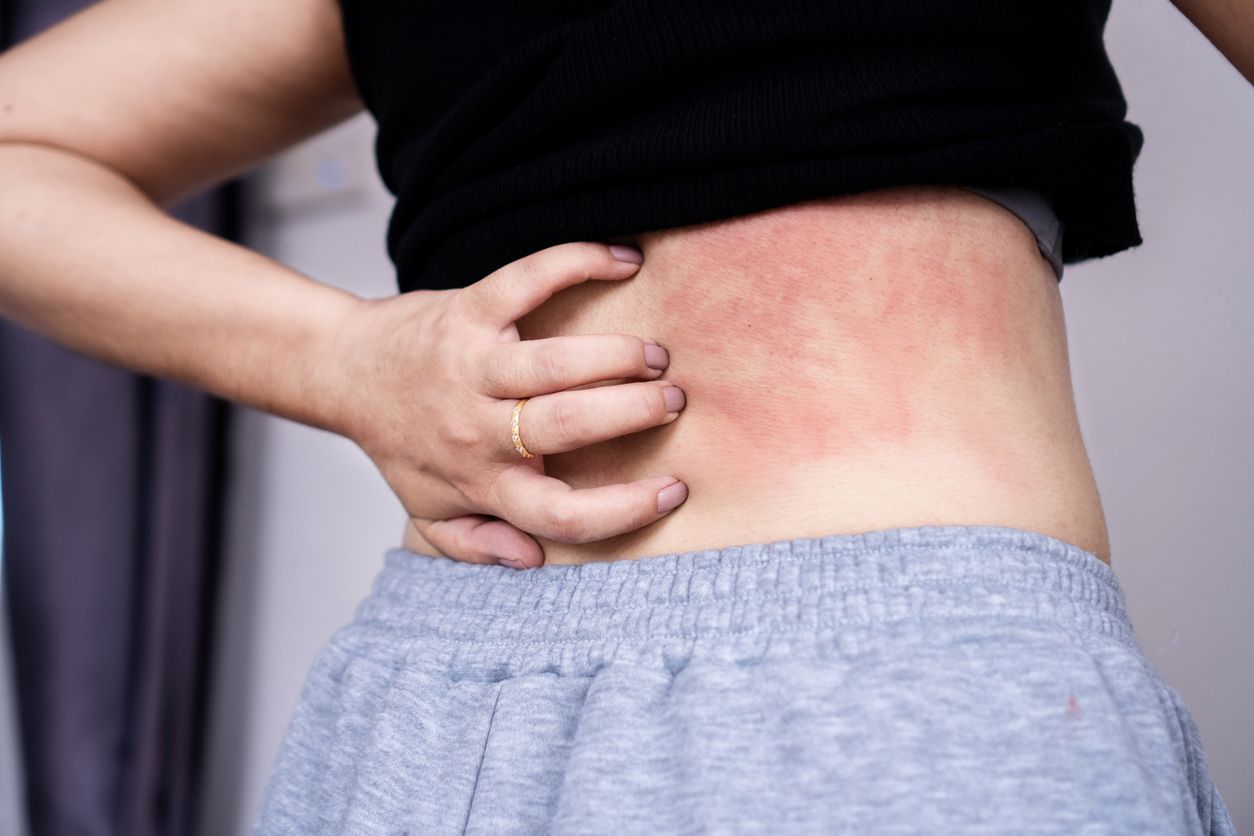
A skin rash is a broad medical term describing various changes to the skin’s appearance, such as alterations in color, texture, or pattern. Rashes may be accompanied by itching, swelling, flaking, or dryness. They can affect small areas or spread across the entire body.
6 Common Causes of Itchy, Red Skin — It's Not Always a Mosquito Bite!
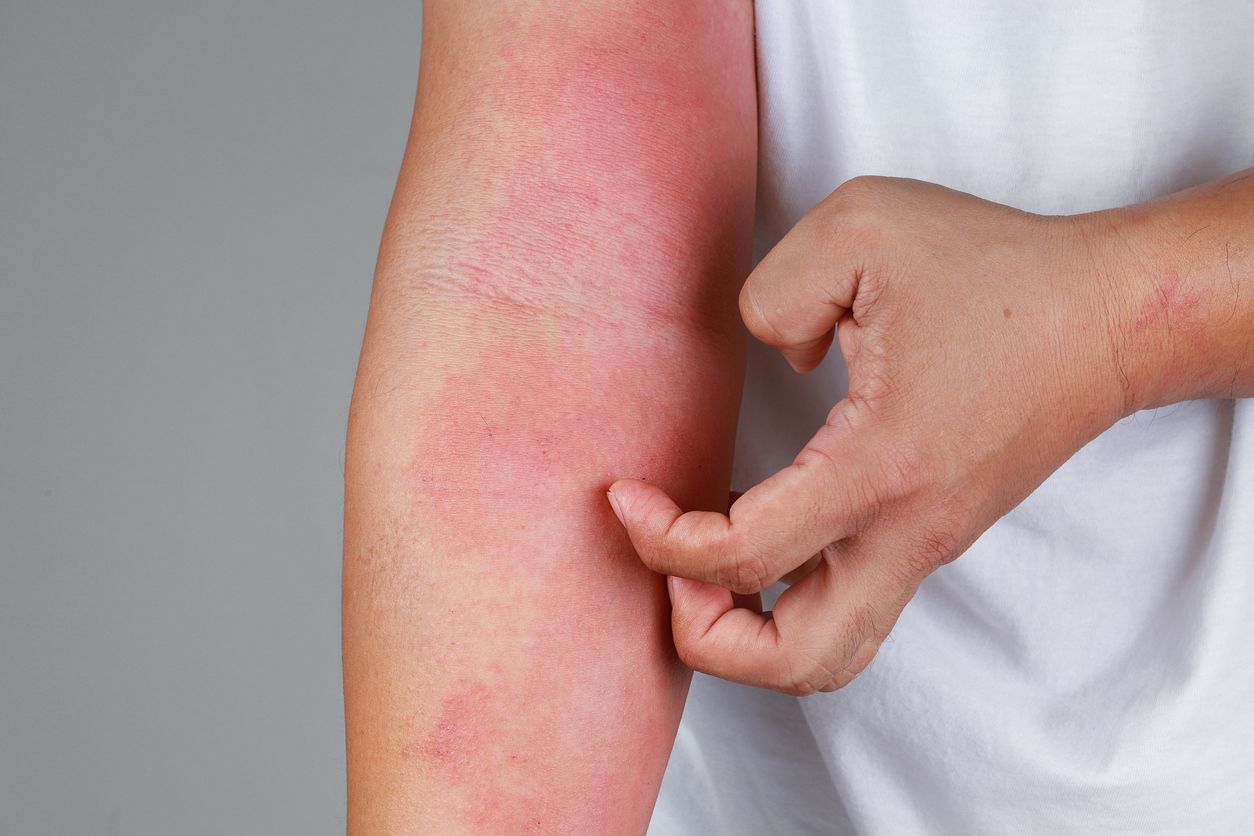
• Allergic reactions: Food, medications, cosmetics, skincare products, cleaning agents, metals, and environmental triggers like pollen, dust mites, and pet dander can all cause allergic skin reactions.
• Chemical irritants: Exposure to household chemicals such as cleaners, disinfectants, laundry detergents, and hair dyes can damage the skin barrier, leading to dryness, redness, itchiness, and flaking. Prolonged exposure, especially on the hands and face, increases the risk.
• Environmental factors: Dry weather, sudden temperature changes, pollution, and UV exposure can irritate the skin. In winter or air-conditioned environments, moisture loss can trigger itching. Airborne allergens and pollutants can also worsen symptoms.
• Psychological factors: Emotional stress, anxiety, tension, or lack of sleep may affect nerve responses, causing itchiness—especially at night or during rest. This type of "psychogenic itch" may occur without visible skin changes.
• Drug allergies (Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis): Certain medications like antibiotics, antipyretics, or anticonvulsants can trigger severe allergic reactions, resulting in rashes, swelling, or in extreme cases, Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN). These often present with systemic symptoms and require immediate medical attention.
• Immune system dysfunction: Autoimmune conditions or immune imbalances, such as lupus, psoriasis, or atopic dermatitis, can cause chronic skin inflammation and itching. Weakened immunity can also lead to increased allergic responses or infections.
免費體驗
Acne Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
The 6 Most Common Types of Skin Rashes — Know the Warning Signs!
1. Acute and Chronic Urticaria (Hives)
Urticaria is marked by sudden, itchy, raised welts that vary in size.
○ Acute urticaria is often triggered by food, medication, infections, allergens, or stress, and typically resolves within 24 hours.
○ Chronic urticaria lasts over 6 weeks and may be linked to autoimmune issues or unknown causes. Both types feature redness, itching, and sometimes burning or swelling.
2. Atopic Dermatitis & Eczema
These chronic, relapsing conditions are common in infants and allergy-prone individuals. Rashes often affect the face, neck, and body folds, accompanied by intense itching, dryness, and flaking. Eczema can result from allergens, irritants, stress, or climate, with irregular rash shapes, blisters, oozing, scaling, or scabbing. It overlaps with atopic dermatitis but has a broader scope.
3. Contact Dermatitis
Caused by direct skin contact with irritants or allergens, this condition falls into two categories:
○ Irritant contact dermatitis results from repeated exposure to substances like detergents, fragrances, or alcohol. Symptoms include dryness, flaking, burning, or cracking.
○ Allergic contact dermatitis occurs when the immune system reacts to allergens like nickel, latex, or preservatives, causing redness, itching, blisters, or oozing—usually localized to the contact area. Treatment involves avoiding triggers and using topical corticosteroids.
4. Viral Rashes & Drug Rashes
○ Drug rashes can arise from allergic reactions to antibiotics, painkillers, or antihypertensives. They often appear a few days after taking the drug, typically symmetrical, and may affect the whole body. Severe cases can escalate into conditions like Stevens-Johnson Syndrome.
○ Viral rashes are common in children or those with weak immunity and are triggered by viruses like enterovirus, roseola, chickenpox, or measles. They often come with fever, sore throat, or swollen lymph nodes.
5. Shingles (Herpes Zoster)
Caused by the reactivation of the chickenpox virus, shingles typically emerges during stress or weakened immunity. It starts with tingling and burning pain, followed by clusters of water-filled blisters arranged in a band-like pattern on one side of the body—often the waist, chest, or face. The rash is painful and can last weeks to months.
6. Insect Bites & Insect-Induced Dermatitis
Insect bites often cause localized allergic reactions with red bumps, swelling, and intense itching—common culprits include mosquitoes, fleas, mites, ants, and midges.
○ Mite bites often affect skin folds or covered areas, with small, recurring rashes.
○ Some people are allergic to proteins in insect saliva, causing larger areas of swelling or hives. Relief methods include cold compresses, antihistamine creams, or oral medication. Avoid scratching to prevent hyperpigmentation or scarring.
Soothing & Treating Skin Rashes: Topical vs Oral Medication
At-home care tips:
• Keep skin clean and dry, but avoid over-cleansing.
• Avoid scratching to prevent infection and inflammation.
• Wear loose, breathable clothing.
• Use gentle, non-irritating cleansers.
• Apply moisturizer to maintain hydration.
• Use cold compresses or wet wraps to relieve itchiness.
Medications:
• Topical treatments: corticosteroids, antihistamine creams, antibiotics, or antifungal ointments—use under medical guidance.
• Oral medications: antihistamines, corticosteroids, antibiotics, or antivirals—prescribed by a doctor.
When to see a doctor:
• Rapidly spreading rash
• Rash with fever, pain, or pus
• Rash interfering with daily life
• No improvement with self-care
7 Habits to Help Prevent Skin Rashes
• Avoid known allergens: Identify and steer clear of triggers.
• Maintain clean, moisturized skin: Use gentle cleansers and moisturize regularly.
• Adopt healthy routines: Balanced diet and adequate sleep boost immunity.
• Manage stress effectively: High stress can compromise the immune system and worsen skin conditions.
• Protect your skin from the sun: UV exposure can irritate rashes—always use sun protection.
• Use gentle skincare products: Avoid alcohol, fragrances, and dyes.
• Keep your environment clean: Wash bedding, pillows, and carpets regularly and use dust mite-proof materials.
免費體驗
Acne Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
Rashes That Won’t Go Away? Try Perfect Medical’s Acne Treatment for a Skin Reset!
Whether it’s pimples, eczema, hives, or drug rashes—Perfect Medical’s Acne Treatment is worth a try. Originally designed for tackling acne, blackheads, scars, clogged pores, dehydration, and dull skin, this non-invasive, painless treatment is safe even for sensitive skin. Once your skin stabilizes, it can also help regulate oil and moisture balance. Now’s the perfect time for a gentle skin renewal!
The treatment uses advanced dual-direction spiral suction and vacuum dermabrasion technology to gently soften and exfoliate dead skin cells, deeply cleanse clogged pores, and infuse purifying serums. It stimulates collagen production from within for radiant, youthful skin.
Book your trial now and enjoy:
✔ Professional skin analysis
✔ Perfect Medical’s Acne Treatment
Try Now: Acne Treatment免費體驗
Acne Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
FAQ

Why do I have bumps on my skin?
Bumps may indicate early inflammation. If left untreated, they could develop into chronic conditions that are harder to resolve.
What causes itchy skin?
Itching is usually caused by external irritants or internal hormonal imbalances.
Are skin rashes contagious?
Rashes from internal causes are not contagious, but those caused by viral infections may be.
Can skin rashes be cured?
Some rashes are curable, while others like eczema or psoriasis tend to recur and require long-term management.
Can I go out in the sun with a skin rash?
Moderate sun exposure can help some skin conditions, but excessive sun can worsen rashes—always apply sun protection.








