
- Home
- Trend
- Weight Loss Strategies
- Acne Tips
- Hair Health Information
- Blemish Removal Tips
- Acne Scar Removal Tips
- Muscle Building Techniques
- Intimate Care Tips
- Postpartum Intimate Care
- Eye Bags Wiki
- Tips for Face Slimming
- Secret of Permanent Hair Removal
- Breast Enlargement Tips
- Cure to Snoring
- Marionette Lines
- Skin-Tightening Secrets
Pigmentation can be triggered by skin injury and inflammation, UV damage, and hormonal fluctuations. Dermatologists note that dark spots on the face or body, including melasma and hyperpigmentation, can be visibly reduced by adopting six daily habits. Learn them now.
Why Does Pigmentation Occur?
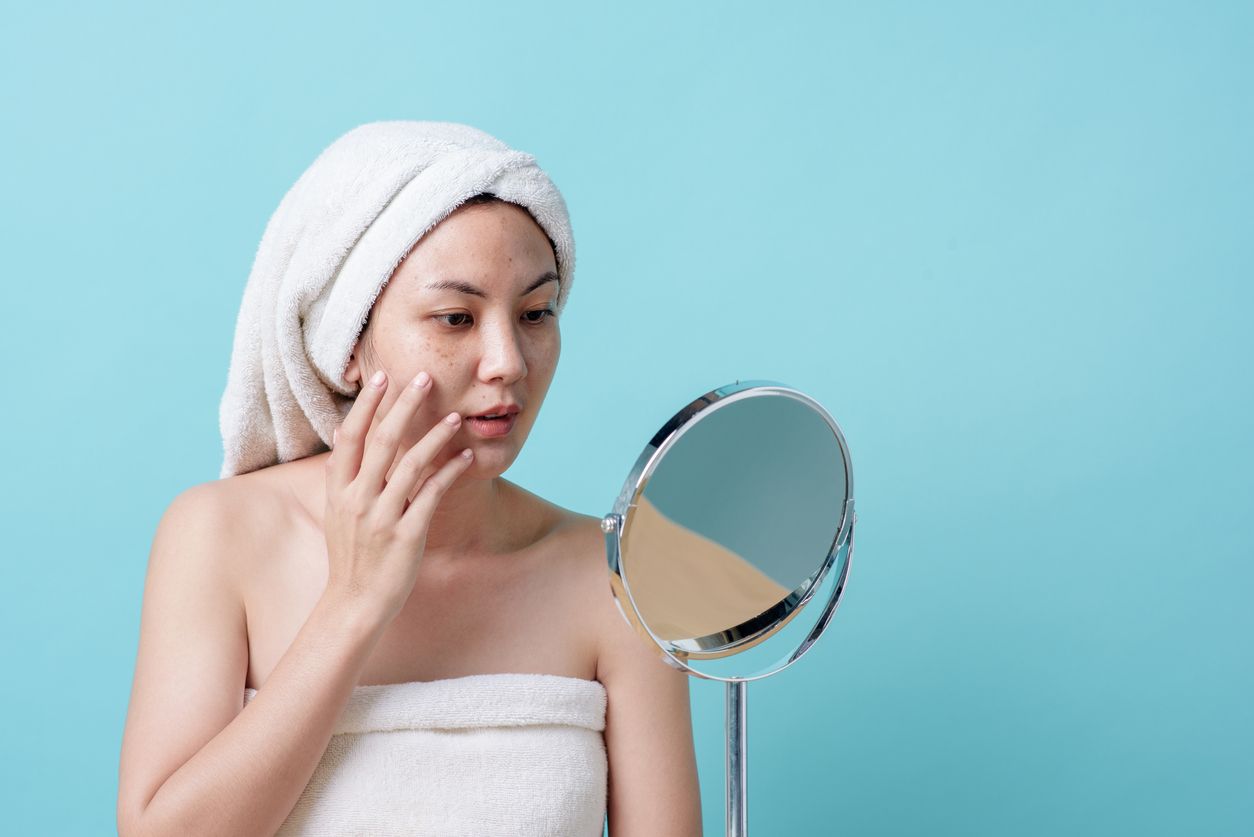

1. UV Damage
Melanin is not the enemy. Melanocytes in the basal layer produce melanin to protect the skin from UV damage and prevent sunburn. However, when the skin is exposed to sunlight, excessive melanin production or slow cellular turnover can cause melanin to accumulate at various levels of the skin. This buildup appears on the surface as visible brown or dark brown spots.
Individuals with darker skin naturally have more melanin, and are therefore less prone to sunburn.
2. Hormonal Stimulation
Hormonal imbalance is a major culprit. Besides UV exposure, pigmentation is also strongly linked to hormone fluctuations.
During the 10 days surrounding ovulation, progesterone levels spike. The brain sends the same signal that stimulates progesterone and melanin production, causing melanocytes to become extremely active. If the metabolism is slow or sun protection is inadequate, excess melanin can be produced, leading to pigmentation.
During menopause, pregnancy, and postpartum, hormonal levels become highly unstable, making melasma (hormonal spots) more likely.
3. Skin Inflammation and Injury
Inflammation from acne, insect bites, cuts, burns, and other forms of skin trauma triggers a series of reactions.
Initially, the skin becomes red due to blood vessel dilation, allowing more repair factors to reach the injured site. This inflammatory response forms a red mark.
As the wound heals, the skin and blood vessels may remain dilated or thickened, leaving red acne marks or scars. Melanin production also increases to protect the weakened skin, causing the marks to turn from red to brown or dark brown. After scabbing and peeling, pigmentation commonly appears.
Types of Pigmentation
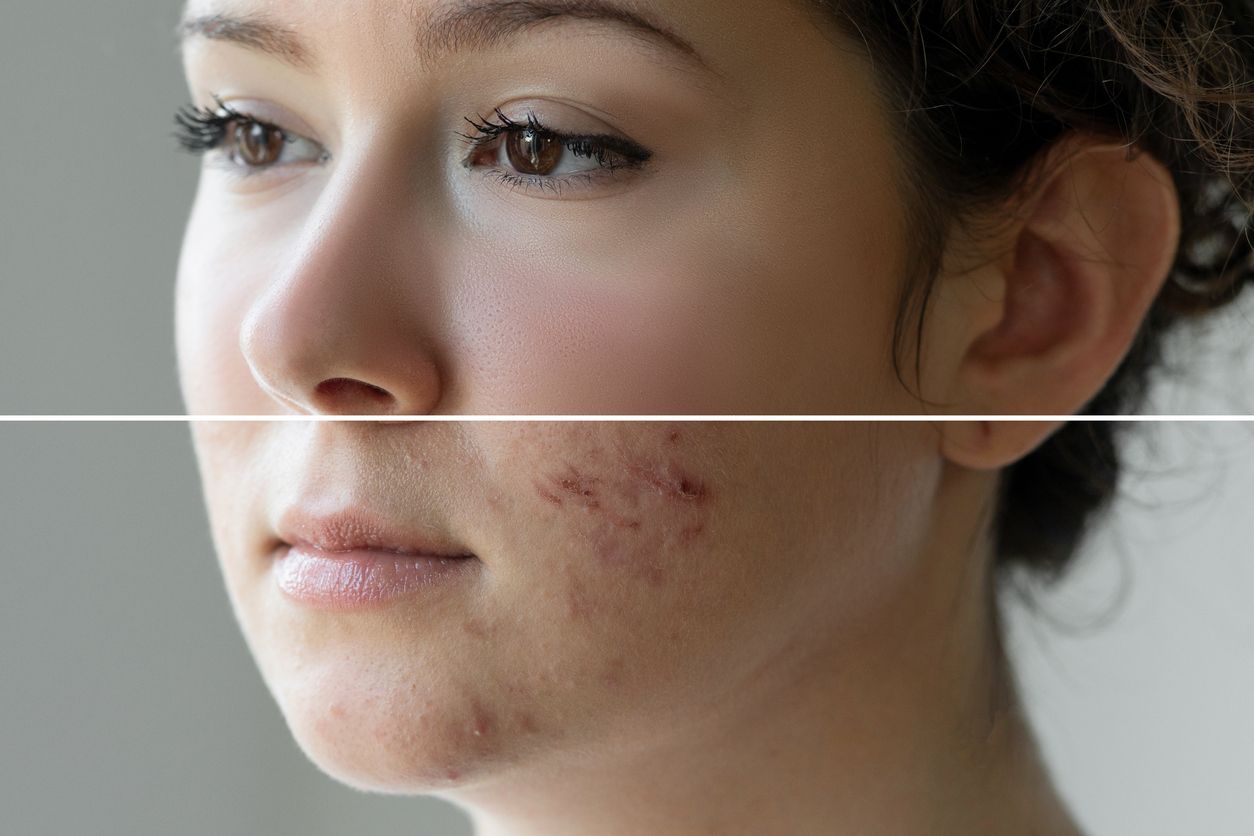
1. Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH)
Pigmentation caused by eczema, injury, acne, and insect bites generally appears in two categories: red marks and brown/black marks.
Red pigmentation indicates the skin is still inflamed and healing. Once healing is complete, brown or dark pigmentation develops.
However, real-life skin is unpredictable—post-inflammatory marks may appear deep red, purple, or even a mix of black and violet due to intertwined melanin, dilated vessels, and thickened tissue.
PIH scars can also be atrophic (indented) or hypertrophic (raised), each requiring different treatment approaches.
2. Pigmented Spots: Melasma
Pigmented spots form when excess melanin accumulates, triggered by various factors including hormonal changes, long-term UV exposure, heat, immune imbalance, slow metabolism, excess free radicals, stress, and obesity.
Among all pigmentation types, melasma is the most challenging to treat because melanin is deposited at multiple depths and lies closely against blood vessels. Laser or heat-based treatments can dilate vessels and overstimulate melanocytes, worsening pigmentation and causing rebound darkening.
3. Long-Term Friction — Underarm Pigmentation
Areas that rarely see sunlight can become darker due to chronic friction and thickened skin. Knees, the backs of knees, heels, and elbows darken easily due to frequent bending, pressure, and friction with fabric and surfaces. Underarm pigmentation is similarly caused by constant friction between the arms and underarm skin.
免費體驗
PicoCure Pigmentation Removal Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
How to Treat Pigmentation: Methods and Improvements
1. Whitening Creams for Pigmentation
Topical formulas can target either red pigmentation or brown/black pigmentation.
• Red PIH: Choose ingredients that calm inflammation and constrict blood vessels—olive leaf extract, green tea extract, azelaic acid, and niacinamide—to soothe inflammation and prevent red marks from turning brown.
• Brown/black PIH: Use vitamin C, kojic acid, arbutin, AHAs, hydroquinone derivatives, retinoids, and tranexamic acid.
Apply whitening creams morning and night to speed up melanin breakdown and prevent red marks from evolving into dark pigmentation.
2. “Vitamin C in the Morning, Vitamin A at Night”
This widely adopted skincare routine means applying vitamin C (or its derivatives) in the morning and vitamin A (retinoids) at night.
This combination controls oxidation during the day and focuses on repair, anti-inflammation, and anti-aging at night—an effective strategy for fading pigmentation and preventing UV-induced darkening.
3. Sun Protection
Skin aging is an inevitable law of nature. Two major factors that accelerate aging are oxygen (free radicals) and UV radiation.
Free radicals form with every breath, attacking DNA. UV exposure increases free radical formation, triggering melanin overproduction and resulting in sunspots or pigmentation. Therefore, consistent sun protection is essential.
4. Dietary Habits
Since free radicals accelerate aging, eating antioxidant-rich foods helps protect skin and regulate melanin production.
Foods rich in vitamins A, B, C, and E, lycopene, carotenoids, polyphenols, anthocyanins, and flavonoids—such as leafy greens, citrus fruits, berries, fatty fish, seeds, and green tea—support better metabolism and help reduce pigmentation.
5. Chemical Peels (AHA Peels)
Excess melanin, keratin, and dilated vessels can be difficult to shed naturally, especially in the body where circulation is slower—body pigmentation may take 6–7 years to fade. AHA peels dissolve the bonds between keratinocytes, soften dead skin, and accelerate skin turnover. This helps fade dark spots, scabs, and pigmentation more quickly.
6. Pico Laser Treatment
Pico laser is one of the most effective and fastest treatments for stubborn pigmentation. Compared with traditional nanosecond lasers, pico lasers deliver ultra-short pulses that shatter melanin more precisely across different skin layers. They generate significantly less heat, reducing the risk of rebound pigmentation and making them suitable even for melasma. Pico particles are pulverized into ultra-fine dust, making them easier for the skin to eliminate.
Shallow pigmentation often shows visible improvement after just one session.
30-Minute Pigmentation Improvement — PicoCure Pigmentation Removal Treatment
When melanin clusters are too large, the skin struggles to metabolize them. The PicoCure US Pico Laser Treatment from Perfect Medical shatters stubborn melanin within 30 minutes, improving pigmentation, dark spots, melasma, red/dark acne marks, uneven tone, and dullness.
Four wavelengths (1064 nm, 650 nm, 585 nm, 532 nm) deliver shockwaves that break melanin at different depths into fine powder. Pigmentation and spots lighten immediately and continue fading with natural metabolism. The treatment is pain-free, non-invasive, and does not trigger rebound darkening.
Pico lasers also stimulate collagen regeneration by breaking down old collagen and promoting new, supple collagen. This boosts hydration, thickens the dermis, refines pores, and restores firm, smooth, luminous skin—instantly making you look younger.
This treatment is internationally certified and trusted by thousands of users and KOLs. It is non-invasive, painless, and suitable for Asian skin. Perfect Medical is offering a free first trial plus a complimentary professional skin analysis.
Grab a Slot: Perfect Medical PicoCure Pigmentation Removal Treatment免費體驗
PicoCure Pigmentation Removal Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
FAQ

Are people with lighter skin more prone to pigmentation?
Darker-skinned individuals naturally have more melanin, making them less prone to sunburn. However, sun tanning and pigmentation relate to lifestyle habits. Dark-skinned individuals can still develop sunburn, tanning, and melasma with age; it is simply less visible.
What causes pigmentation?
Main causes include skin injury and inflammation, cumulative UV damage, and hormonal fluctuations. After inflammation, melanocytes produce melanin to protect healing skin. UV damage builds melanin at deeper levels, causing spots that later surface. Hormonal changes also stimulate melanin and slow metabolism.
Why is melasma so difficult to treat?
Melasma spreads widely across multiple skin layers and often connects to micro-blood vessels. Proper treatment requires analyzing melanin depth with imaging devices and selecting wavelengths carefully.
If pigmentation worsens after treatment, the method must be discontinued.
Pico lasers reduce heat damage and are less likely to cause rebound darkening.
How do you treat pigmentation?
Options include whitening creams (vitamin C, kojic acid, arbutin, AHAs, hydroquinone derivatives, retinoids, tranexamic acid), the “C AM / A PM” skincare routine, sun protection, pico laser treatments, and high-concentration AHA peels. These methods improve melanin metabolism and stimulate collagen regeneration.








