
- Home
- Trend
- Weight Loss Strategies
- Acne Tips
- Hair Health Information
- Blemish Removal Tips
- Acne Scar Removal Tips
- Muscle Building Techniques
- Intimate Care Tips
- Postpartum Intimate Care
- Eye Bags Wiki
- Tips for Face Slimming
- Secret of Permanent Hair Removal
- Breast Enlargement Tips
- Cure to Snoring
- Marionette Lines
- Skin-Tightening Secrets
Have you ever noticed splotches or patches on your skin that just don't seem to match your natural tone? These pigmented spots and discoloration can be a source of frustration. But worry not! This guide will delve into the science behind these skin concerns, exploring the causes, impacts, and most importantly, effective management strategies. Get ready to reclaim your radiant, even-toned complexion!
What is a Pigmented Spot? Types and Causes of These Discoloured Skin Patches
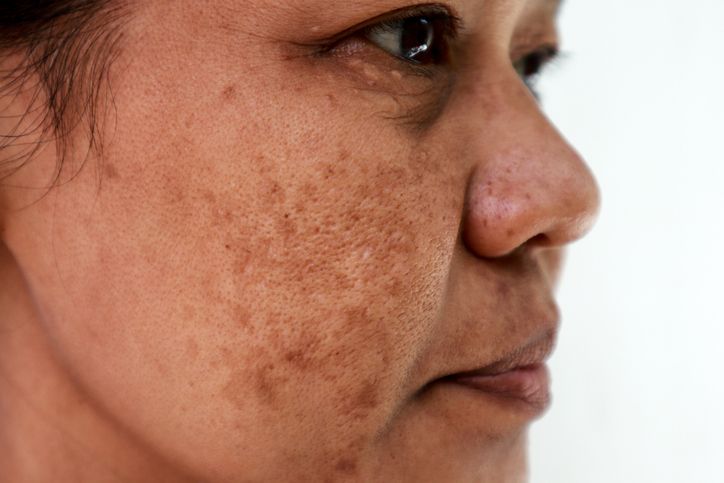
Pigmented spots are areas of the skin that have darker coloration compared to the surrounding skin. They can manifest in various forms, including melasma, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, age spots, and liver spots.
Melasma
This condition is characterised by symmetrical patches of darkened skin, commonly occurring on the face, particularly on the cheeks, forehead, nose, and upper lip. Melasma is often triggered by hormonal changes, such as those during pregnancy or due to the use of birth control pills, which can lead to increased production of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin coloration.
Sun exposure and UV rays
Factors such as sun exposure and UV rays play a significant role in the development of pigmented spots. UV radiation can stimulate melanin production in the skin as a protective mechanism against sun damage. However, excessive or prolonged sun exposure can lead to an overproduction of melanin, resulting in the formation of dark spots and patches.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal changes, particularly those related to female sex hormones like oestrogen, can also influence pigmentation. For example, pregnancy-related hormonal shifts can cause melasma (also known as the "mask of pregnancy") due to increased melanin production triggered by hormonal fluctuations.
Skin Injuries and Post-inflammatory Hyperpigmentation
Additionally, skin injuries, infections, and inflammatory conditions can contribute to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. When the skin undergoes trauma or inflammation, such as from acne breakouts or eczema flare-ups, it may produce excess melanin during the healing process, leading to darkened areas on the skin.
How do I Tell If I Have Pigmented Spots or Other Skin Conditions?
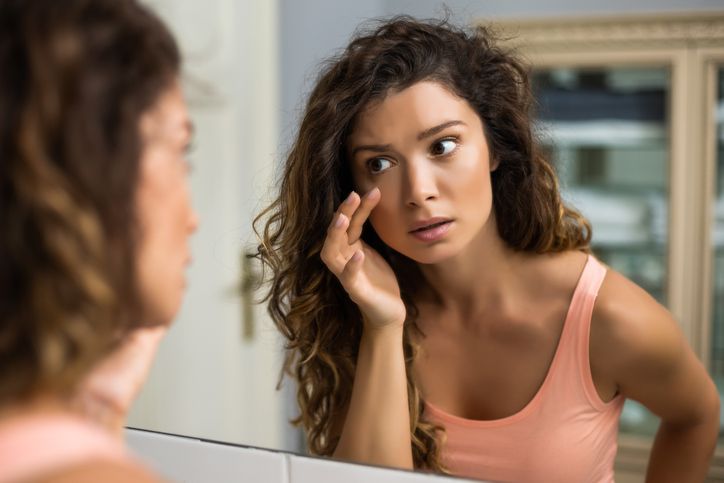

Differentiating between pigmented spots and other skin conditions involves considering various factors such as appearance, texture, location, and associated symptoms. Here are some guidelines to help you distinguish pigmented spots from other skin issues:
1. Appearance
Pigmented spots typically appear as darker or discoloured areas on the skin, ranging from light brown to black. They may be flat or slightly raised and often have a well-defined border. Other skin conditions like rashes, eczema, or psoriasis may present as red, inflamed patches with varying textures.
2. Texture
Pigmented spots are usually smooth to the touch, especially if they are age spots or sunspots. Skin conditions like warts, moles, or skin tags may have a different texture, such as roughness, raised areas, or a wart-like appearance.
3. Location
Pigmented spots tend to appear on areas of the skin exposed to sun, such as the face, hands, shoulders, and arms. They can also occur in areas prone to friction or pressure. Other skin conditions may have specific locations or distributions. For instance, eczema often affects flexural areas like the elbows and knees, while fungal infections may appear in moist areas like the groyne or between toes.
4. Associated Symptoms
Pigmented spots usually do not cause symptoms like itching, pain, or changes in size unless they are malignant or precancerous. Skin conditions such as dermatitis, psoriasis, or fungal infections may cause itching, redness, inflammation, or changes in texture.
5. History and Progression
Knowing the history and progression of the skin issue can be helpful. Pigmented spots may develop gradually over time with sun exposure or ageing. Other skin conditions may have specific triggers, patterns of recurrence, or changes in appearance over time.
免費體驗
PicoCure Pigmentation Removal Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
Skin Pigmentation and its Impact on our Skin Colour and Skin Health
Pigmentation issues, such as melasma, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, age spots, and liver spots, can have significant impacts on skin health and appearance. Here's a detailed elaboration on their effects:
1. Skin Tone
Pigmented spots contribute to an uneven skin tone, causing certain areas to appear darker or discoloured than others. This unevenness can create a patchy or mottled appearance, diminishing the skin's natural radiance and uniformity. Over time, persistent pigmentation issues can make the skin look dull, aged, and less vibrant.
2. Skin Texture
Beyond affecting skin tone, pigmentation problems can also impact skin texture. Areas with dark spots or patches may feel rough, uneven, or bumpy to the touch. This texture irregularity can be particularly noticeable in cases of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, where the skin has undergone previous inflammation or injury, leading to surface imperfections.
3. Overall Appearance
The presence of pigmented spots can significantly alter the overall appearance of the skin. These spots can detract from the skin's smoothness and clarity, creating distractions or focal points that draw attention away from the skin's natural beauty. For individuals dealing with visible pigmentation issues, concerns about their skin's appearance can lead to reduced self-confidence and impact their overall quality of life. Addressing pigmentation concerns can not only improve the skin's appearance but also boost confidence and well-being.
4. Risk of Skin Cancers
One of the significant concerns associated with pigmentation issues is their link to an increased risk of certain types of skin cancers, such as basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. While pigmented spots themselves are not cancerous, they can indicate sun damage and prolonged UV exposure, which are risk factors for developing these types of skin cancers.
• Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC): This type of skin cancer often appears as a raised, pearly bump or a pinkish patch of skin. BCC is typically slow-growing and rarely spreads to other parts of the body but can cause local tissue damage if left untreated.
• Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC): SCC may present as a scaly or crusty growth, a red patch, or a sore that doesn't heal. It can grow and spread more aggressively than BCC, potentially metastasizing to nearby lymph nodes or organs if not diagnosed and treated promptly.
Prevention and Protective Measures to Stop Yourself From Getting Darker Skin Tones
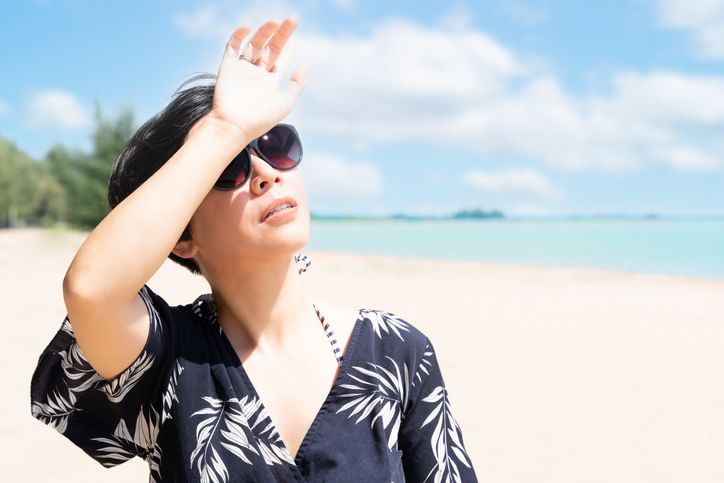

Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is a significant contributor to the development of pigmented spots, including age spots, sunspots, and melasma. UV rays stimulate melanocytes in the skin to produce melanin, leading to increased pigmentation and the formation of dark spots over time. Prevention and protective measures are crucial in managing and reducing the formation of pigmented spots on the skin. Here's a detailed elaboration on sun protection practices:
Sun Protection Strategies
• Use of Sunscreen: Applying a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF (Sun Protection Factor) is one of the most effective ways to protect the skin from UV damage. Broad-spectrum sunscreens protect against both UVA and UVB rays, which are responsible for skin ageing and sunburn, respectively. Reapply sunscreen every two hours, especially if sweating or swimming.
• Wearing Protective Clothing: Covering exposed skin with clothing, such as long-sleeved shirts, pants, wide-brimmed hats, and sunglasses, provides physical protection against UV rays. Clothing with UPF (Ultraviolet Protection Factor) ratings offers additional sun protection.
• Seeking Shade: Limiting direct sun exposure, especially during peak hours when UV intensity is highest (typically between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.), can reduce the risk of UV-induced pigmentation. Seek shade under trees, umbrellas, or awnings when outdoors.
• Using Sun-Protective Accessories: Accessories like umbrellas, sun hats with wide brims, and sunglasses with UV protection lenses help shield the skin and eyes from harmful UV rays. Specialised clothing and swimwear with built-in UV protection are also available.
Avoiding Excessive UV Exposure
• Tanning beds and sunlamps: These are artificial sources of UV radiation that should be avoided due to their potential harm to the skin. UV radiation from tanning beds can penetrate deep into the skin, causing damage that manifests as pigmented spots, premature ageing signs like wrinkles and fine lines, and an increased risk of developing various types of skin cancers.
• Be precautious outdoor: Reflective surfaces such as water, snow, sand, and concrete have the ability to reflect and amplify UV rays, leading to heightened UV exposure. This amplified exposure can occur even on cloudy days or in shaded areas, making it essential to take extra precautions when spending time in these environments.
Consistency and Persistence
• Daily Sun Protection: Incorporate sun protection into your daily skincare routine, regardless of the weather or season. UV rays can penetrate clouds and cause skin damage even on cloudy days.
• Year-Round Protection: Maintain sun protection practices year-round, not just during summer months. UV radiation can still reach the skin during winter, especially at higher altitudes and in regions with snow cover.
Educational Awareness
Educating Others : Spread awareness about the importance of sun protection and its role in preventing pigmented spots, skin ageing, and skin cancers. Encourage family, friends, and colleagues to adopt sun-safe behaviours.
By adopting these sun protection strategies and making them a consistent part of your daily routine, you can significantly reduce the risk of pigmented spot formation, protect your skin from UV damage, and promote long-term skin health.
4 Solutions to Treat Hyperpigmentation and Make Your Skin Lighter
When it comes to managing pigmented spots and skin pigmentation disorders, a range of treatment options is available, each tailored to address specific concerns. These treatments encompass topical creams and serums, chemical peels for exfoliation, and advanced laser therapy and light treatments for targeted correction. Let's delve into these treatment approaches in detail:
1. Topical Creams and Serums
Topical treatments are often the first line of defence against pigmented spots. They typically contain active ingredients that target melanin production and promote skin renewal. Common ingredients include:
• Kojic Acid: Known for its skin-lightening properties, kojic acid inhibits melanin synthesis, reducing pigmentation.
• Vitamin C: As a potent antioxidant, vitamin C not only brightens the skin but also helps reduce melanin production, fading dark spots over time.
• Hydroquinone: This ingredient is effective in lightening pigmented spots by hindering melanin production.
These topical treatments are applied directly to the affected areas, allowing for targeted treatment and gradual improvement in skin pigmentation.
2. Chemical Peels
Chemical peels involve the application of a chemical solution to exfoliate the outer layer of the skin, revealing smoother and more even-toned skin underneath. Peels containing alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) such as glycolic acid and beta hydroxy acids (BHAs) like salicylic acid can help lighten pigmented spots and improve overall skin texture.
3. Laser Therapy and Light Treatments
Advanced laser technologies offer precise and effective solutions for pigmented spot removal and skin pigmentation disorders. One such technology is the Picoway Picosecond Laser Treatment, which utilises picosecond laser pulses to target melanin in the skin:
• Picosecond Laser: This technology delivers short-pulsed laser energy, shattering melanin particles for natural metabolic removal. It is non-invasive, painless, and can rapidly reduce pigmentation issues such as melasma, acne scars, and dark spots.
• IPL (Intense Pulse Light): IPL treatments emit various wavelengths of intense light to target and dissolve melanin, effectively reducing superficial pigmentation. However, IPL is less effective for dermal pigmentation and melasma compared to laser treatments.
• PicoWay Picosecond Laser: This treatment is suitable for Asian skin tones and addresses stubborn skin discolorations without damaging the surrounding skin. It provides significant dark spot reduction with minimal side effects and no rebounding pigmentation.
4. Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) and Remedies
In addition to modern treatments, traditional remedies and TCM practices may be considered for managing pigmentation:
• TCM: Chinese medicine practitioners may recommend herbal teas, dietary changes, and lifestyle adjustments to address underlying factors contributing to hyperpigmentation.
• Natural Remedies: While lemon juice and certain topical creams can help lighten pigmented spots, it's important to note that these remedies should be used cautiously, as excessive sun exposure post-treatment can lead to pigmentation formation.
Choosing the Right Treatment
The choice of treatment depends on factors such as the severity of pigmentation, skin type, and individual preferences. Consultation with a dermatologist or skincare professional is essential to determine the most suitable treatment plan tailored to your specific needs and goals.
Aftercare and Maintenance
Regardless of the treatment chosen, post-treatment care is crucial for optimal results:
• Sun Protection: Protect your skin from UV exposure to prevent pigmentation rebounding and maintain treatment outcomes.
• Moisturise: Keep the skin well-hydrated and nourished with moisturisers suitable for your skin type.
• Follow Professional Recommendations: Adhere to aftercare instructions provided by your skincare provider, including lifestyle adjustments and skincare product recommendations.
免費體驗
PicoCure Pigmentation Removal Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
Regain Healthy Skin And Say Goodbye to Dark Patches With The Right Move!
Understanding the causes and effects of pigmented spots and skin pigmentation disorders is the first step in effective management. By incorporating preventive measures, treatment approaches, holistic management strategies, and seeking the suitable interventions when needed, individuals can take proactive steps towards healthier, even-toned skin.
PicoCure Pigmentation Removal Treatment免費體驗
PicoCure Pigmentation Removal Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
FAQ

1. How can treatments effectively address hyperpigmentation in skin conditions?
Hyperpigmentation treatment involves targeting melanin production and promoting cell turnover. Topical treatments with kojic acid and vitamin C are effective in fading dark spots and achieving lighter skin tones. Additionally, professional procedures like chemical peels exfoliate dead skin cells, leading to healthier skin and reduced pigmentation disorders.
2. What role do chemical peels play in improving skin condition and reducing hyperpigmentation?
Chemical peels are instrumental in promoting healthier skin by exfoliating dead skin cells and stimulating cell renewal. They help fade dark spots and pigmentation disorders, leading to a lighter and more even skin tone. Proper selection of the peel type and strength is essential based on individual skin condition and treatment goals.
3. How does kojic acid contribute to reducing hyperpigmentation and achieving lighter skin?
Kojic acid, a skin-lightening agent, inhibits melanin production, making it effective in fading dark spots and reducing hyperpigmentation. When incorporated into skincare products or topical treatments, kojic acid targets affected skin areas, promoting a lighter tone and healthier skin appearance over time.
4. What factors influence pigmentation disorders and the appearance of affected skin?
Pigmentation disorders can result from sun exposure, hormonal changes, and underlying skin conditions. Sun-exposed areas are particularly susceptible to pigmentation issues due to UV damage, leading to darker spots and uneven skin tone. Hormonal changes, such as those during pregnancy or due to birth control pills, can also contribute to pigmentation changes and affect the appearance of the skin.
5. Are there natural ways to achieve lighter skin tones and reduce hyperpigmentation?
Incorporating ingredients like vitamin C and antioxidants into skincare routines can promote healthier skin cells and fade dark spots naturally. Protecting sun-exposed areas with SPF and avoiding excessive UV exposure is crucial to prevent pigmentation disorders and maintain a lighter skin tone. Additionally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet and hydration supports overall skin health and reduces hyperpigmentation over time.








