- Home
- Trend
- Weight Loss Strategies
- Acne Tips
- Hair Health Information
- Blemish Removal Tips
- Acne Scar Removal Tips
- Muscle Building Techniques
- Intimate Care Tips
- Postpartum Intimate Care
- Eye Bags Wiki
- Tips for Face Slimming
- Secret of Permanent Hair Removal
- Breast Enlargement Tips
- Cure to Snoring
- Marionette Lines
- Skin-Tightening Secrets

免費體驗
Acne Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
Acne is a pervasive skin condition that extends beyond facial concerns, affecting various parts of the body. One prevalent and often overlooked form is back acne, or bacne, which can be both uncomfortable and aesthetically concerning. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of back acne, exploring its causes, treatments, and how factors like dead skin cells, clogged pores, and hormonal imbalances contribute to its development.
1
How Back Acne Is Formed?
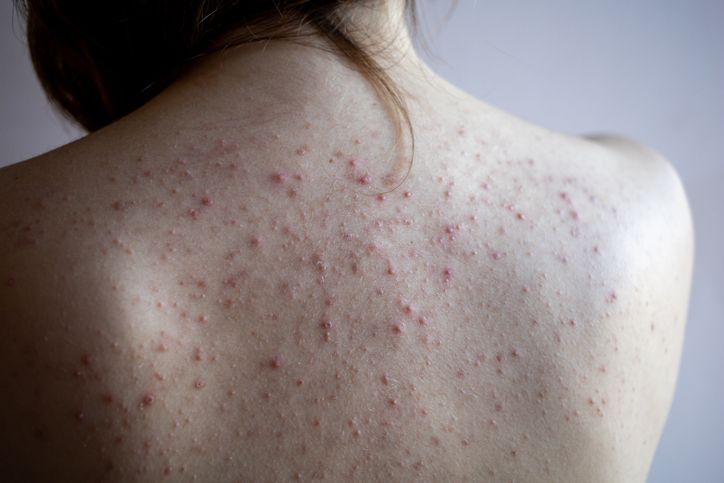
Back acne, a manifestation of body acne, tends to be overlooked in discussions, often overshadowed by its more visible facial counterpart. Despite its less apparent nature, back acne can pose persistent and troublesome challenges.
The formation of back acne is intricately linked to the occurrence of clogged pores. Accumulated dead skin cells, oils, and other substances create a milieu where hair follicles and pores become obstructed. This obstruction serves as a breeding ground for acne, establishing an environment conducive to its formation. The back, with its unique anatomy and higher prevalence of sebaceous glands, becomes susceptible to the development of acne lesions. This process not only affects the skin's appearance but also contributes to the persistence of back acne, necessitating targeted skincare strategies for effective prevention and management. Understanding the underlying mechanisms of back acne formation is crucial for implementing tailored approaches that address the specific challenges posed by this distinct subset of body acne.

2
What Are the Different Types of Acne Lesions Seen in Back Acne?
Back acne, like facial acne, presents with various types of lesions that provide insights into the severity and nature of the condition. Recognizing these lesions is essential for understanding the specific challenges associated with back acne.
1. Papules
Papules are small, raised bumps on the skin without a visible centre. They can be red or pink in colour.
Significance: Papules in back acne indicate inflammation and clogged pores. While they may be less severe than other lesions, they contribute to the overall appearance of acne.
2. Pustules
Pustules are similar to papules but contain a visible centre filled with pus. They often appear as white or yellowish bumps with red bases.
Significance: Pustules indicate a more advanced stage of inflammation. The presence of pus suggests bacterial involvement, and these lesions can be more noticeable and potentially more painful.
3. Nodules
Nodules are large, solid, painful lumps beneath the surface of the skin. They are deeper and more severe than papules and pustules.
Significance: Nodules in back acne signify deep inflammation and often leave behind scars. They can be particularly challenging to treat and may require medical intervention.
By understanding what you have on your back, it helps you in managing skincare and pinpoint the issue faster. The combination of these lesions in varying degrees contributes to the overall presentation of back acne.
3
What Causes Back Acne & What Makes Back Acne Worse?

While musculoskeletal and skin diseases may not be direct causes of back acne, they can contribute to its development or exacerbate existing conditions. Here are some factors that might be involved:
1. Friction and Irritation: Continuous friction between clothing and the skin, especially tight or non-breathable fabrics, can lead to irritation and contribute to the formation of acne on the back.
2. Excessive Sweating: Sweat, when not properly managed, can create a conducive environment for acne. The combination of sweat, dead skin cells, and oils can clog skin pores and lead to acne breakouts.
3. Hormonal Fluctuations: Hormonal changes, particularly during puberty, menstruation, or hormonal imbalances, can trigger an overproduction of sebum (skin oil), leading to clogged pores and acne.
4. Genetics: There may be a genetic predisposition to acne. If your family has a history of acne, you might be more prone to developing it, including on the back.
5. Poor Hygiene: Inadequate cleansing of the back, especially for sweaty skin that engaged in activities that lead to dirt and bacteria accumulation, can contribute to acne formation.
6. Diet: While the direct link between diet and acne is debated, some studies suggest that diets high in dairy or certain carbohydrates may contribute to acne development.
7. Cosmetic Products: The use of certain cosmetic or skincare products that are comedogenic (tend to clog pores) can contribute to back acne. This is especially true if these products are not thoroughly removed.
8. Medications: Some medications, such as certain steroids or drugs that affect hormone levels, may contribute to acne as a side effect.
9. Stress: While stress itself may not directly cause acne, it can exacerbate existing conditions. Stress can lead to hormonal fluctuations and may impact overall skin health.
It's essential to recognize that back acne is often multifactorial, meaning several factors may contribute simultaneously. Addressing these potential causes and maintaining a consistent and appropriate skincare routine can help manage and prevent back acne.

4
Navigating the Hormonal Roller-coaster: Prevent The Chance of Back Acne Spreading to Face Acne
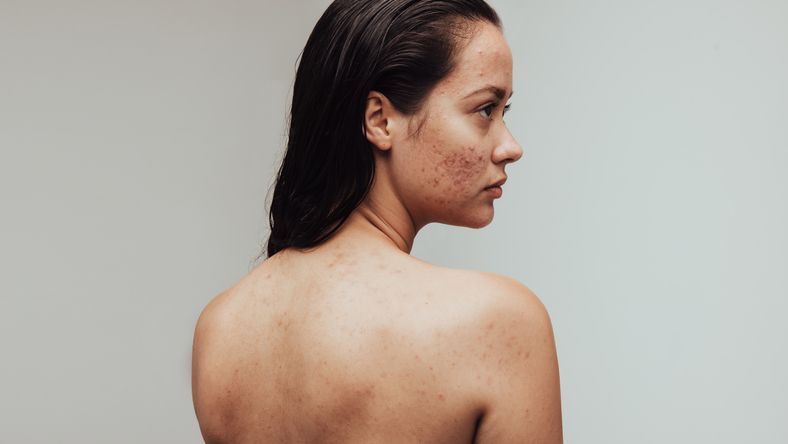

While some individuals may experience both back acne and facial acne simultaneously, others may only have one or the other, as acne can manifest in various forms and locations on the body, and it can differ from person to person.
Factors such as genetics, hormonal fluctuations, lifestyle, and skincare practices can influence the occurrence and distribution of acne. Some people may be more prone to developing acne on their face, while others may experience it predominantly on their back, chest, shoulders, or other areas.
It's also worth noting that the causes of facial acne and back acne can overlap, such as hormonal imbalances, excessive sebum production, and certain lifestyle factors. However, the specific combination of factors leading to acne can vary from person to person.

免費體驗
Acne Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
5
Topical Treatment Options to Treat Back Acne & Face Acne

If you have back acne
Salicylic Acid Salicylic acid, a powerful component in acne-fighting products, plays a crucial role in unclogging pores, eliminating dead skin cells, and reducing inflammation. Its effectiveness proves invaluable in addressing and combating back acne.
Oral Antibiotics Systemic antibiotics, such as tetracycline or doxycycline, may be prescribed to address bacterial factors contributing to back acne. These medications work internally to combat infection and inflammation.
Isotretinoin (Accutane) Isotretinoin is a potent oral medication reserved for severe cases of acne, including back acne. It works by reducing sebum production, preventing clogged pores, and addressing inflammation. Due to its potential side effects, its usage is closely monitored.
For both Back and Face Acne
Oral Antibiotics Oral antibiotics serve as an additional option for managing acne. These medications are prescribed to address bacterial factors contributing to acne development. It's important to follow your healthcare provider's guidance on usage and dosage.
Retinoids Retinoids are useful in treating both back and face acne. These topical medications, derived from vitamin A, work by promoting cell turnover, preventing the clogging of pores, and reducing inflammation. Incorporating retinoids into your skincare routine can contribute to clearer and healthier skin.
Benzoyl Peroxide Benzoyl peroxide, another potent acne-fighting agent, operates by eliminating bacteria, reducing inflammation, and preventing new breakouts. Maximising its benefits involves understanding how and when to use it effectively.
In addressing acne, whether on the back or face, it's essential to tailor your treatment approach to your specific needs.

6
Other Treatment Options to Treat Back Acne & Face Acne
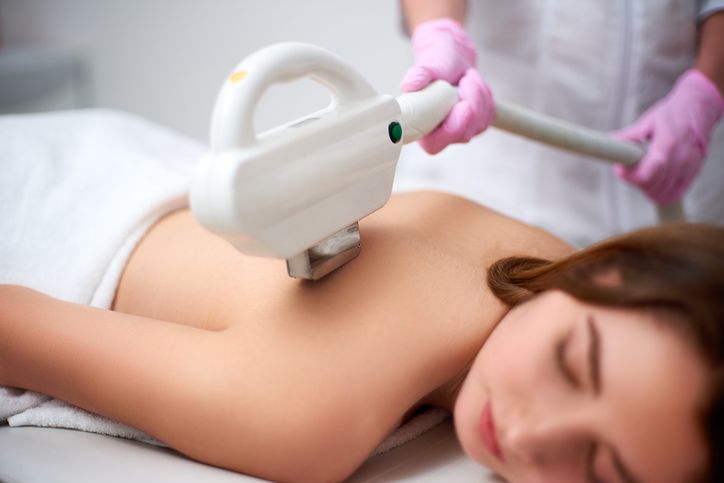
If you have back acne
Laser Therapy Laser therapy emerges as a promising option for back acne treatment. By targeting specific light wavelengths, it aims to reduce inflammation and bacteria, fostering clearer skin.
Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) PDT involves the application of a photosensitizing agent, followed by exposure to specific light wavelengths. This method can effectively target and destroy acne-causing bacteria and reduce inflammation on the back.
If you have face acne like hormonal acne / adult acne
Perfect Medical's Acne Treatment Specifically designed for acne-prone skin, this treatment targets a range of concerns including blemishes, blackheads, whiteheads, pockmarks, enlarged pores, dry skin, and acne scars. Using dual spiral suction and drainage echnology, it gently removes dead skin cells and unclogs pores, soothing inflammation and infection caused by acne. The treatment includes a medical-grade hydrating serum that penetrates deep into the skin, providing hydration and nourishment while regulating sebaceous glands to prevent excess oil production.
Chemical Peels Chemical peels, performed by dermatologists, involve applying a solution to the skin to exfoliate the outer layer. This can improve the appearance of acne scars, even out skin tone, and reduce active acne.
Light Therapy Light therapies, including blue light and red light treatments, are designed to target bacteria and inflammation associated with acne. These can be effective for managing inflammatory acne on the face.
7
Dietary Choice You Should Try to Reduce Severe Acne
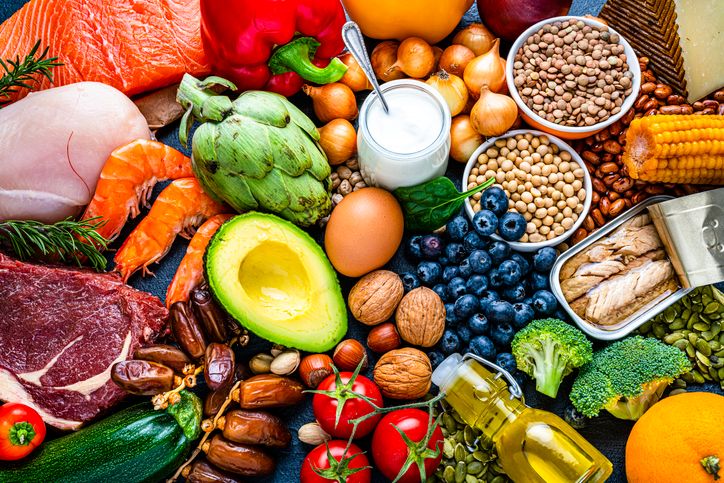

While there is no direct "acne cure" in specific foods, maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet can contribute to overall skin health, which may indirectly help soothe both back and facial acne. Here are some dietary considerations:
1. Antioxidant-rich foods
Examples: Berries, tomatoes, carrots, spinach.
Role: Antioxidants help combat oxidative stress in the body, which can contribute to skin inflammation. Including a variety of colourful fruits and vegetables can provide a range of antioxidants.
2. Omega-3 fatty acids
Examples: Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), flaxseeds, walnuts.
Role: Omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties. Including sources of these healthy fats in your diet may help reduce inflammation associated with acne.
3. Probiotics
Examples: Yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut.
Role: Probiotics promote a healthy gut microbiome, which is linked to skin health. A balanced gut flora may help reduce inflammation and support the immune system.
4. Zinc-rich foods
Examples: Pumpkin seeds, lentils, chickpeas.
Role: Zinc is known to have anti-inflammatory properties and plays a role in wound healing. Including zinc-rich foods may support skin health.
5. Vitamin A-rich foods
Examples: Sweet potatoes, carrots, kale.
Role: Vitamin A is essential for skin health and may help regulate sebum production. Including foods rich in beta-carotene, a precursor to vitamin A, can be beneficial.
On the other hand, some individuals find that certain foods can trigger acne breakouts. It's important to pay attention to your body's response to different foods and make adjustments accordingly. Common triggers for some people include dairy products, high-glycemic foods, and excessive consumption of sugary or processed foods.

8
What You Should Not Wear to Avoid Aggravating Back Acne

As the location of back acne is quite different from the face acne, what we wear actually affects the condition of it. Here are a few things you should prevent:
1. Tight clothing
Wearing tight clothing can contribute to the worsening of back acne by trapping sweat and irritating the skin. Tight garments create a warm and humid environment, promoting the proliferation of acne-causing bacteria. The friction between the fabric and the skin can lead to increased inflammation, making existing acne more uncomfortable and potentially causing new breakouts. Choosing breathable fabrics such as cotton and opting for loose-fitting clothing allows for better air circulation, reducing the likelihood of sweat accumulation. It's also advisable to avoid tight straps or accessories that may rub against the back, as this can contribute to irritation and further aggravate acne.
2. Non-breathable fabrics
Avoiding non-breathable fabrics, such as synthetic materials like polyester, is crucial to prevent back acne from worsening. These fabrics can trap heat and moisture, creating an environment that encourages bacterial growth and clogged pores. Opting for natural fibres like cotton or moisture-wicking fabrics can help keep the back dry and reduce the risk of acne flare-ups.
3. Heavy backpacks
Carrying heavy backpacks or bags that constantly rub against the back can contribute to friction and irritation, potentially worsening existing acne. It's advisable to choose backpacks with padded straps or distribute the weight evenly across both shoulders to minimise pressure and friction on the back.
4. Harsh or irritating fabrics
Fabrics that are harsh or irritating to the skin, such as wool or certain synthetic blends, can exacerbate back acne. These materials may cause friction and irritation, leading to increased inflammation. Choosing softer fabrics that are gentle on the skin can help minimise the risk of irritation and discomfort.
5. Prolonged wet clothing
Prolonged contact with wet clothing, especially after sweating or swimming, can contribute to back acne. Wet clothing can further irritate the skin and create an environment conducive to bacterial growth. Changing out of wet clothes promptly and maintaining good hygiene practices can help prevent the worsening of back acne.
By being mindful of clothing choices and making adjustments to minimise factors that contribute to irritation and moisture retention, individuals can play a proactive role in managing and preventing the exacerbation of back acne.

免費體驗
Acne Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
9
Conclusion

In conclusion, understanding and treating back acne involve a multifaceted approach. By addressing factors like dead skin cells, clogged pores, and hormonal imbalances, individuals can take proactive steps to achieve clearer, healthier skin, and remember to fix them before they turn into horrendous scars!

免費體驗
Acne Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
FAQ

1. Can dead skin cells cause back acne?
Yes, dead skin cells can contribute to back acne by clogging pores. Regular exfoliation helps remove these cells, reducing the risk of acne.
2. How common is body acne?
Body acne, including back acne, is more common than you might think. it affects a significant percentage of the population, with varying severity.
3. Is salicylic acid safe for all skin types?
Salicylic acid is generally safe for most skin types. However, individuals with sensitive skin should start with lower concentrations to avoid irritation.
4. How long does it take to see results with prescription treatments?
The timeframe for seeing results with prescription treatments varies. It may take several weeks to months before significant improvement is noticeable.
5. What role do sebaceous glands play in back acne?
Sebaceous glands produce sebum, an oily substance that can contribute to back acne when produced excessively. Balancing sebum production is essential for preventing acne.