
- Home
- Trend
- Weight Loss Strategies
- Acne Tips
- Hair Health Information
- Blemish Removal Tips
- Acne Scar Removal Tips
- Muscle Building Techniques
- Intimate Care Tips
- Postpartum Intimate Care
- Eye Bags Wiki
- Tips for Face Slimming
- Secret of Permanent Hair Removal
- Breast Enlargement Tips
- Cure to Snoring
- Marionette Lines
- Skin-Tightening Secrets
Tetracycline has become a savior for many acne sufferers. Acne is a common skin condition that doesn’t only affect teenagers—some people continue to break out even in their 40s. With advances in medical science, tetracycline antibiotics have stood out among various acne treatments for being cost-effective, clinically effective, and relatively low in side effects. In this article, we’ll take a close look at how tetracycline works, its potential side effects, and what you should be aware of when using it.
Let’s Start with the Basics: How Does Acne Form?
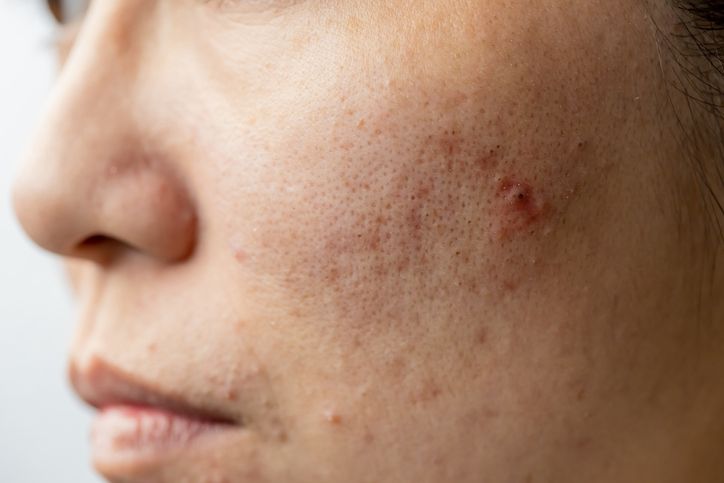
Main Cause 1: Excess Sebum Production
Sebaceous glands in the skin produce oil to protect the skin from bacteria, dirt, and environmental damage, as well as to retain moisture and regulate temperature. But when oil production becomes excessive—due to genetics, hormonal imbalance, or a greasy diet—pores can easily become clogged, triggering acne.
Main Cause 2: Clogged Pores
It’s not just excess oil; dead skin cells, dirt, and bacteria can also clog hair follicles. Once a follicle is blocked, sebum can't exit properly, causing inflammation and leading to pimples or even cystic acne.
Main Cause 3: Bacterial Infection
Cutibacterium acnes (formerly Propionibacterium acnes) is a common acne-causing bacteria. Normally, it exists in small numbers on the skin, but when pores are blocked and oxygen is limited, the bacteria multiply rapidly. Hormonal changes—like those during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause—further fuel sebum production, creating a perfect environment for bacteria to thrive. Infected acne often becomes red, swollen, pus-filled, and painful.
Main Cause 4: Weakened Immune System
A compromised immune system—caused by stress, lack of sleep, dehydration, illness, aging, or side effects from medications—can increase inflammation and even trigger allergic-like responses to food, releasing histamines that make skin red and itchy. A weak immune defense also struggles to fight off acne-causing bacteria, increasing the chance of breakouts.
What Exactly Is Tetracycline? 5 FAQs About This Acne Treatment
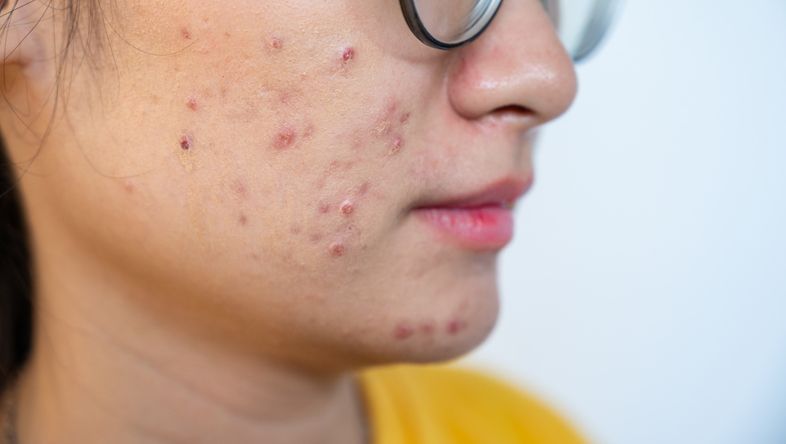
Q1. What is tetracycline?
Tetracycline is an antibiotic used to kill or prevent the growth of bacteria. It’s effective for infections like UTIs, ear infections, sinusitis, bronchitis, and oral infections—but not viral illnesses. Antibiotics can be applied topically or taken orally. For mild acne, topical antibiotics (like erythromycin or clindamycin) combined with good hygiene and habits may suffice. But for persistent, bacteria-driven acne, long-term oral tetracyclines may be needed to control inflammation and skin damage.
Q2. Is tetracycline effective for acne?
Yes. Tetracycline treats bacterial acne, rosacea, and general skin inflammation. Since acne tends to relapse, tetracycline works not only by killing C. acnes but also by reducing inflammation and modulating the immune system to prevent future breakouts. It also fights a broad range of other bacteria, including Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, rickettsiae, chlamydia, mycoplasma, and certain protozoa.
Q3. What types of tetracycline are available?
First-generation tetracycline (tetracycline hydrochloride) is a basic, low-cost oral antibiotic with anti-inflammatory properties—often the first choice for acne. However, it must be taken on an empty stomach and shouldn’t be combined with dairy or iron supplements, or it loses effectiveness. Resistance is also common. Newer versions, like doxycycline and minocycline, are better tolerated and more effective, with fewer dietary restrictions.
Q4. How long do you need to take tetracycline?
Treatment typically lasts 4–6 weeks, sometimes up to 3 months. In the early stages, acne may not improve immediately or may even worsen—this is normal. Be patient and don’t stop the medication on your own once symptoms improve; consistent use is key to success.
Q5. Why can’t you stop tetracycline abruptly?
Antibiotics need to be taken as prescribed to ensure full effectiveness. Stopping midway can lead to bacterial resistance, reducing the drug’s effectiveness. Self-medicating can also lead to choosing the wrong drug, causing unnecessary side effects like killing healthy bacteria, weakening immunity, or allowing harmful bacteria to mutate and become more difficult to treat.
免費體驗
Acne Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
Six Key Tips for Taking Tetracycline Safely
1. Be aware of possible side effects
Common side effects include gastrointestinal upset (e.g., constipation or diarrhea) and increased sensitivity to sunlight. First-generation tetracycline is excreted through feces, while newer versions are excreted via urine. Ask your doctor which kind you’re prescribed. Tetracycline may also cause pigmentation or dark spots from sun exposure, so sun protection is essential, though not everyone experiences this.
2. Not safe for pregnant women or young children
Tetracycline is not recommended for pregnant or breastfeeding women or children under 8. It can impair bone and tooth development in fetuses and infants, leading to discoloration or enamel defects. Alternative antibiotics should be prescribed in such cases.
3. Avoid if you have poor kidney function
If your kidneys don’t function well, tetracycline can cause blue-gray skin discoloration or tooth staining over time. Doxycycline, which doesn’t rely on kidney metabolism, may be a safer alternative—but always drink plenty of water to reduce stomach irritation.
4. Prescription only
Tetracyclines are prescription medications. Your doctor will consider the severity of your acne, type of infection, medical history, allergies, and overall health before prescribing to ensure safe and effective treatment.
5. Avoid combining with aluminum, magnesium, or calcium
Tetracycline’s absorption is affected by these minerals, commonly found in milk, antacids, and supplements. Wait 2–3 hours after consuming these before taking tetracycline. Also, it may reduce the effectiveness of birth control pills—use other contraception methods if necessary.
6. Follow pre- and post-use guidelines
Always check the expiration date—expired tetracycline can cause kidney damage or autoimmune reactions like lupus. Store in a cool, dry place. Don’t lie down right after taking it to avoid acid reflux. Since it increases sun sensitivity, use sunscreen and limit sun exposure after taking the medication.
Worried About Tetracycline’s Side Effects? Try a Safer, Stress-Free Alternative — Perfect Medical’s Acne Treatment
Tetracycline is an effective acne solution, but some people worry about side effects or drug resistance from stopping too early. With continuous advancement in medical aesthetics, there’s a non-drug option worth considering.
Perfect Medical’s Acne Treatment uses spiral suction drainage technology combined with medical-grade essence infusion. It first removes dirt, oil, and dead skin cells to prevent pore blockage and breakouts, then nourishes the skin with deep hydration to restore oil-water balance.
The treatment also boosts collagen in the skin’s deeper layers, improving elasticity, shrinking pores, and leaving you with youthful, dewy, flawless skin. Click below to claim your free trial now—don’t miss out!
Experience Perfect Medical Acne Treatment免費體驗
Acne Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
FAQ

What’s the typical tetracycline dosage and frequency?
Traditional tetracycline: 500 mg capsules, taken on an empty stomach, 4 times daily. Minocycline: 100 mg capsules, taken twice a day—usually limited to a few months to prevent side effects like skin or tooth discoloration. Doxycycline: Similar to minocycline, 100 mg twice daily. Dosage must always follow a dermatologist’s prescription.
Can I drink anything other than water when taking tetracycline?
Warm water is best—it helps the medicine reach your stomach quickly and reduces irritation. Avoid juices, milk, coffee, or drinks with calcium or iron, which affect absorption. If you’re taking other medications, consult your doctor to avoid harmful interactions.
What triggers acne and pimples?
Besides the root causes discussed earlier, lifestyle habits also play a major role. A diet high in sugar, oil, or dairy can inflame the skin. Poor cleansing, irritating skincare products, or constantly touching your face can worsen acne. Stress also contributes by disrupting sleep and hormone levels.
What should I know before taking tetracycline?
You must see a doctor and get a valid prescription to avoid counterfeit drugs and incorrect usage. Everyone reacts differently—some improve, others may worsen. A professional diagnosis ensures safer, more tailored treatment. If one medication doesn’t work, your doctor can suggest a better alternative.
Which is better: Tetracycline or Isotretinoin (Aczone)?
Oral isotretinoin (A-acid) is also used for severe acne. It controls oil production, reduces inflammation, and kills acne bacteria. If tetracycline doesn’t work, your doctor may suggest isotretinoin. However, isotretinoin has more side effects—initial flare-ups, dry mucous membranes, and more—so professional supervision is crucial.








