
- Home
- Trend
- Weight Loss Strategies
- Acne Tips
- Hair Health Information
- Blemish Removal Tips
- Acne Scar Removal Tips
- Muscle Building Techniques
- Intimate Care Tips
- Postpartum Intimate Care
- Eye Bags Wiki
- Tips for Face Slimming
- Secret of Permanent Hair Removal
- Breast Enlargement Tips
- Cure to Snoring
- Marionette Lines
- Skin-Tightening Secrets
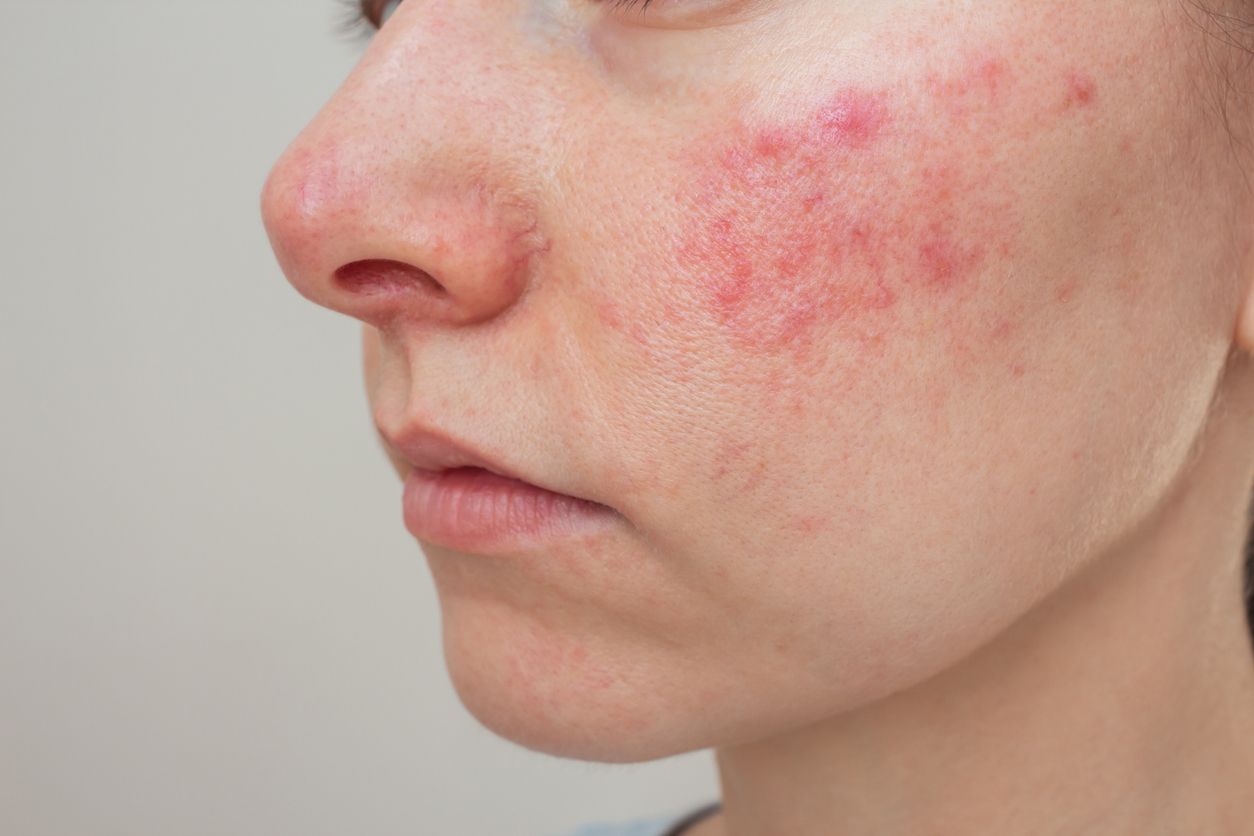
What should you do if you have rosacea? Also known as rosacea dermatitis or acne rosacea, this chronic skin condition often appears as persistent redness across the face — especially around the nose. While rosacea skin may look harmless, it’s actually a form of long-term inflammation that can flare up repeatedly and may indicate deeper imbalances in the body.
Here’s everything you need to know: the 4 main types of rosacea, plus dermatologist-approved treatment and care solutions to help calm inflammation and restore healthy, resilient skin.
Understanding Rosacea: More Than Just Facial Redness — It’s a Chronic Skin Condition

“Rosacea,” also known as rosacea dermatitis or rosacea rash, is a chronic inflammatory skin disorder that primarily affects the face. It tends to flare up and subside periodically, making it challenging to completely cure. Many people confuse it with simple facial flushing, but rosacea redness is often more intense, long-lasting, and accompanied by other symptoms such as visible capillaries or acne-like bumps.
The severity and appearance of rosacea vary from person to person, but common symptoms include facial redness, flushing, visible blood vessels, red bumps, or even eye-related symptoms that can become serious if left untreated.
Understanding the different subtypes of rosacea helps identify your skin condition more accurately and allows for better, targeted treatment.
The 4 Main Types of Rosacea — Recognize the Signs and Treat Accordingly
1. Erythematotelangiectatic Rosacea (ETR): This is the most common type of rosacea, characterized by frequent flushing that develops into persistent redness over time — mainly on the cheeks, nose, forehead, and chin. Fine, visible blood vessels (spider veins) often appear. The skin tends to be sensitive and may experience stinging or burning sensations.
2. Papulopustular Rosacea: Often mistaken for acne, this type features red bumps and pustules without blackheads. The skin feels tender, hot, or inflamed, and flare-ups may last for weeks.
3. Phymatous Rosacea: This form affects the nose, leading to thickened skin, nodules, and swelling — causing the nose to appear bulbous (a condition known as rhinophyma). It’s more common among men.
4. Ocular Rosacea: This type impacts the eyes and surrounding areas, causing dryness, redness, burning, itching, and in severe cases, eyelid inflammation or conjunctivitis. Some people even experience eye symptoms before any visible facial redness appears.
Tip: Some patients exhibit more than one subtype at the same time, which is why professional dermatological diagnosis is crucial for proper management.
6 Major Causes of Rosacea: When Your Skin Signals an Internal Imbalance
1. Genetic Predisposition: Research suggests rosacea may run in families, meaning genetics can play a role in its development.
2. Vascular Hypersensitivity: The facial blood vessels of rosacea-prone individuals tend to be more reactive, dilating easily in response to stimuli and causing persistent redness.
3. Immune System Dysregulation: The skin’s immune system can overreact to environmental triggers, resulting in inflammation.
4. Demodex Mites: These tiny mites naturally live in human hair follicles, but in excess, they can trigger inflammation or worsen rosacea symptoms.
5. Helicobacter Pylori (H. pylori): Some studies suggest a possible connection between this stomach bacterium and rosacea, though research remains inconclusive.
6. Common Triggers That Can Worsen Rosacea: Identifying and avoiding triggers can help reduce flare-up frequency and severity. These may include:
○ Extreme temperatures (hot or cold)
○ Sun exposure and UV radiation
○ Emotional stress or anxiety
○ Spicy foods and alcohol
○ Hot drinks like coffee or tea
○ Harsh skincare ingredients (alcohol, fragrance, menthol, witch hazel)
○ Intense exercise
○ Certain medications (e.g., vasodilators)
○ Heavy or occlusive makeup
免費體驗
Acne Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
6 Steps to Manage Rosacea Daily — Gentle Skincare Is Key
While rosacea cannot be completely cured, proper daily care and the right skincare routine can help control symptoms, minimize flare-ups, and maintain a comfortable, healthy complexion.
1. Choose Gentle, Non-Irritating Cleansers: Avoid products with soap, alcohol, or fragrance. Use low-foam or non-foaming cleansers with a skin-friendly pH to protect the skin barrier.
2. Use Lukewarm Water: Extreme water temperatures can trigger redness — stick to mild, body-temperature water for cleansing.
3. Pat Dry Instead of Rubbing: Gently press your face dry with a soft towel; avoid rubbing or stretching the skin.
4. Keep Skin Well-Hydrated: Moisturizing is essential to strengthen the barrier and reduce irritation. Use fragrance-free, alcohol-free moisturizers or creams to soothe redness.
5. Always Wear Sunscreen: UV rays are one of rosacea’s top triggers. Use a physical (mineral) sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher — ideally one formulated for sensitive skin, containing zinc oxide or titanium dioxide.
6. Avoid Harsh Exfoliants or Active Ingredients: Skip products containing acids, salicylic acid, retinoids, or harsh scrubs — they may worsen inflammation.
3 Medical Treatment Options for Rosacea: Tackling Mites and Redness at the Root
1. Identify and Avoid Personal Triggers
○ Keep a daily log of your diet, activities, and environmental factors to find patterns.
○ Once identified, minimize exposure to known triggers.
2. Prescription Treatments (Under Dermatologist Guidance)
○ Topical Medications: Dermatologists may prescribe gels or creams like metronidazole, azelaic acid, or ivermectin to reduce redness and inflammation.
○ Oral Medications: For more severe cases, oral antibiotics (such as tetracyclines) or other prescription drugs may be recommended.
○ Ocular Rosacea Treatment: Eye drops or oral medication may be prescribed if the eyes are affected.
3. Laser and Light Therapies (for Persistent Redness & Visible Veins)
○ Pulsed Dye Laser (PDL): Effective for visible capillaries and chronic redness.
○ Intense Pulsed Light (IPL): Helps improve flushing, pigmentation, and vascular issues.
○ KTP Laser: Targets dilated blood vessels to even out skin tone.
Don’t Panic — Perfect Medical’s Acne Treatment Gently Soothes and Stabilizes Rosacea-Prone Skin!
If you’re struggling with rosacea or similar inflammatory skin conditions, Perfect Medical’s Acne Treatment offers a safe, effective solution that helps calm, cleanse, and rebalance the skin — even for those with high sensitivity.
Using advanced dual-directional spiral suction and vacuum microdermabrasion technology, this treatment deeply cleanses the pores, removes impurities, and regulates sebum balance without pain or downtime. It also boosts collagen renewal to strengthen the skin barrier and improve overall texture and radiance.
Whether you’re dealing with redness, acne, blackheads, or enlarged pores, Perfect Medical’s professional treatment can help restore clarity and calm to your skin.
Experience Now: Acne Treatment免費體驗
Acne Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
FAQ

1. Is rosacea caused by drinking alcohol?
No. Even people who don’t drink can develop rosacea.
2. Is rosacea the same as adult acne?
No. Papulopustular rosacea may look like acne, but it has no blackheads and often comes with redness and visible blood vessels.
3. How many types of rosacea are there?
Four — erythematotelangiectatic, papulopustular, phymatous, and ocular rosacea.
4. Can rosacea be cured?
It’s difficult to eliminate completely, but with proper care and medical treatment, symptoms can be well controlled and greatly reduced.
5. What foods should people with rosacea avoid?
Avoid spicy or very hot foods and drinks, as they can trigger flushing and redness.








