- Home
- Trend
- Weight Loss Strategies
- Acne Tips
- Hair Health Information
- Blemish Removal Tips
- Acne Scar Removal Tips
- Muscle Building Techniques
- Intimate Care Tips
- Postpartum Intimate Care
- Eye Bags Wiki
- Tips for Face Slimming
- Secret of Permanent Hair Removal
- Breast Enlargement Tips
- Cure to Snoring
- Marionette Lines
- Skin-Tightening Secrets
Frequent urination is a common yet often distressing condition that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life and mental well-being. Those who experience the constant need to urinate may find their daily routines disrupted, leading to embarrassment, anxiety, and fatigue. This challenge can result in sleep disturbances, particularly when nighttime urination, or nocturia, becomes a regular occurrence. The physical discomfort and psychological strain associated with frequent urination can deter people from social activities, affecting their overall emotional health.
The Most Common Causes of Frequent Urination

Frequent urination can arise from a variety of factors, each influencing the urinary experience in different ways:
Overactive Bladder Syndrome (OAB)
OAB is a primary culprit behind frequent urination. This condition is marked by an urgent need to urinate, often accompanied by involuntary bladder contractions.
People with OAB may find themselves urinating more than eight times a day and experiencing sudden urges that can lead to urinary incontinence. The unpredictability of OAB can significantly impact daily activities, causing anxiety and discomfort. In addition to OAB, other leading causes of frequent urination include:
1. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
UTIs can irritate the bladder, leading to increased urinary frequency, urgency, and discomfort during urination. Symptoms often include pain or burning sensations while urinating, cloudy or foul-smelling urine, and sometimes even fever. The inflammation and irritation caused by the infection can make it difficult to hold urine, prompting more frequent bathroom visits.
2. Enlarged Prostate (Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia - BPH)
For men, BPH is a common condition characterised by the enlargement of the prostate gland, which can restrict urine flow. This restriction often leads to frequent urination, particularly at night (nocturia), as well as difficulty starting or stopping the urinary stream.
3. Interstitial Cystitis
Also known as painful bladder syndrome, interstitial cystitis causes chronic bladder pressure and pain, leading to an urgent need to urinate. The symptoms can mimic those of a UTI, but without the presence of an infection.
Other Potential Causes
Beyond the common causes mentioned, several additional factors can contribute to frequent urination:
Medications
Diuretics, commonly prescribed for conditions such as hypertension and heart failure, increase urine production, leading to more frequent bathroom trips. Other medications, such as certain antidepressants and blood pressure medications, can also affect urinary frequency.
Pregnancy
During pregnancy, especially in the first and third trimesters, increased pressure on the bladder from the growing uterus can lead to heightened urinary frequency. Hormonal changes also play a role in bladder sensitivity.
Diabetes
Uncontrolled diabetes can result in increased urination, known as polyuria, due to elevated blood sugar levels. The body attempts to expel excess glucose through urine, leading to more frequent trips to the bathroom.
Nervous System Disorders
Conditions like multiple sclerosis or spinal cord injuries can disrupt nerve signals between the bladder and the brain, resulting in bladder control problems and increased urgency.
Dietary Factors
Certain foods and beverages can irritate the bladder. Caffeine, alcohol, and acidic foods may increase urinary frequency. Spicy foods and artificial sweeteners have also been reported to exacerbate bladder issues in some individuals.
Psychological Factors
Anxiety and stress can lead to changes in urinary patterns. Some individuals may experience an increase in urgency and frequency during stressful situations or may have a fear of not making it to the restroom in time.
Bladder Conditions
Conditions such as bladder stones or bladder cancer, though less common, can also contribute to increased urinary frequency and discomfort.
Not Sure If You Urinary Frequently? Check These 10 Symptoms
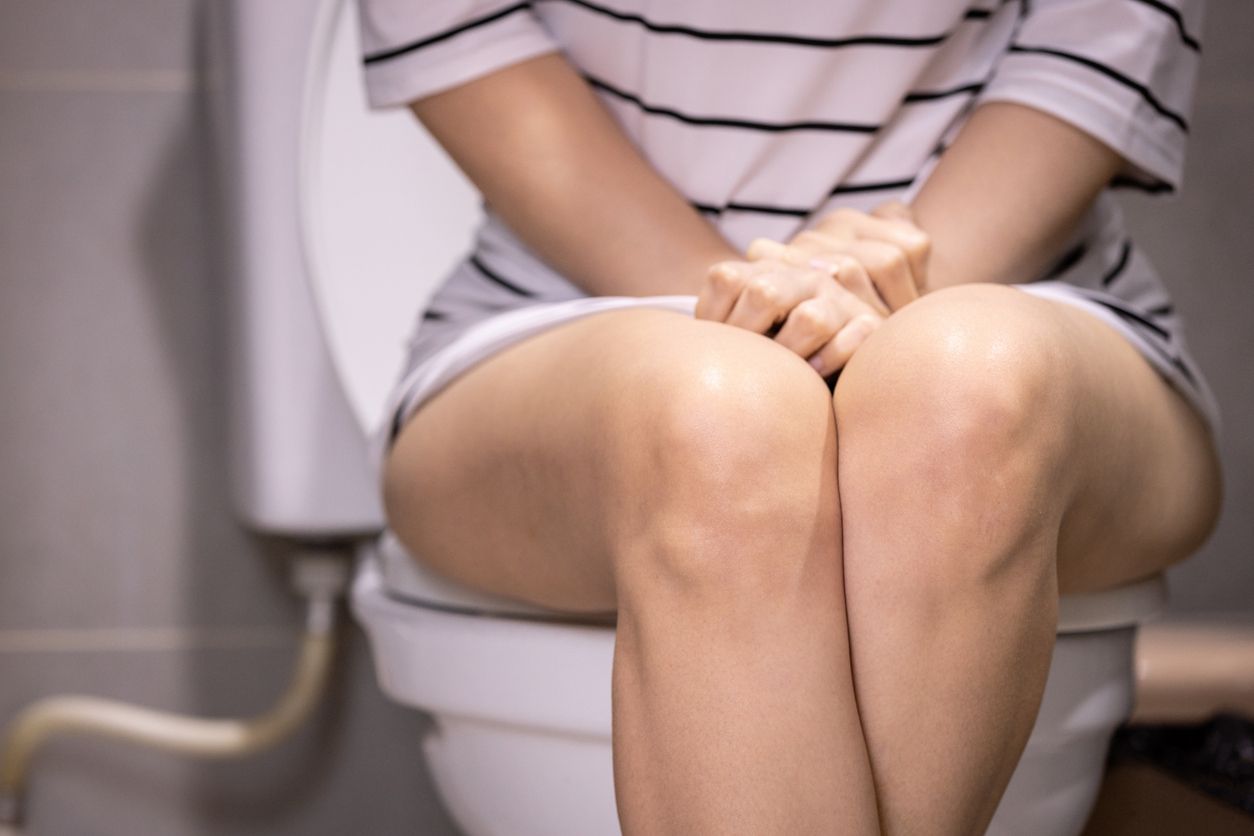
One of the primary symptoms of frequent urination is an urgent need to urinate, often accompanied by discomfort or a feeling of pressure in the bladder. This urgency can strike unexpectedly, making it challenging to manage daily activities or maintain social engagements. Individuals may feel a sudden, overwhelming desire to use the restroom, which can lead to anxiety about being far from a bathroom. This symptom is particularly distressing when it interrupts work, social gatherings, or leisure activities.
Recognizing the Impact of Nighttime Urination
Frequent nighttime urination (nocturia) can significantly affect sleep quality and overall health. Waking up multiple times during the night to urinate disrupts restful sleep, leading to daytime fatigue, irritability, and reduced overall well-being.
People may find themselves feeling exhausted and unable to concentrate during the day. If nighttime urination becomes frequent—often defined as waking up two or more times at night—it’s crucial to discuss this symptom with a healthcare provider, as it can be indicative of underlying health issues.
Additional Symptoms to Monitor
In addition to urgency and nighttime urination, there are several other symptoms associated with frequent urination that individuals should be aware of:
Increased Urinary Frequency
This refers to needing to urinate more than the usual number of times throughout the day—often defined as more than eight times within 24 hours.
Urinary Urgency
A strong, sudden urge to urinate that can be difficult to control. This may occur even if the bladder isn’t full.
Pain or Discomfort During Urination
Dysuria, or pain during urination, can accompany frequent urination. This symptom may indicate a urinary tract infection (UTI) or other bladder issues.
This includes involuntary leakage of urine, which can occur when the urge to urinate is too strong or unexpected.
Straining to Urinate
Difficulty initiating urination or needing to strain to empty the bladder can be a sign of underlying conditions, such as an enlarged prostate or pelvic floor disorders.
Changes in Urine Appearance
Cloudy, dark, or foul-smelling urine can indicate a UTI or other urinary issues. Any noticeable changes should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
Blood in Urine
Hematuria, or blood in the urine, is a serious symptom that requires immediate medical attention, as it can indicate various underlying health concerns.
Increased Thirst
If frequent urination is accompanied by increased thirst, it may be a sign of diabetes or other metabolic conditions.
Bowel Issues
Some people may experience constipation or changes in bowel habits, as pelvic floor disorders can affect both urinary and bowel function.
免費體驗
BTL Emsella Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
Diagnosing the Underlying Issue
Diagnosing the underlying cause of frequent urination involves a comprehensive evaluation that may include physical exams and diagnostic tests.
Steps Involved in a Thorough Medical Evaluation
A healthcare provider will typically take a detailed medical history, asking about urinary habits, symptoms, and any relevant health conditions. The evaluation may also involve:
Physical Exam: A physical examination can help assess potential underlying issues affecting urinary function.
Blood Tests: These tests can determine if underlying conditions such as diabetes or kidney problems are contributing to frequent urination.
Documenting Urinary Patterns
Keeping a bladder diary can be an effective tool in understanding urinary patterns. By recording the frequency, volume, and circumstances surrounding each instance of urination, people can provide valuable information to their healthcare providers for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
2 Treatment Options: Lifestyle Changes or Advanced Solution
Once the underlying causes of frequent urination have been identified, various treatment options can be explored.
1. Discussing Lifestyle Adjustments
Lifestyle modifications can play a significant role in managing urinary frequency. Simple changes include:
Managing Fluid Intake: Understanding how much fluid to consume throughout the day can help regulate urinary frequency. It may be beneficial to avoid excessive fluid intake, especially before bedtime.
Avoiding Irritants: Reducing or eliminating irritants such as caffeine and alcohol can help alleviate symptoms. These substances can stimulate the bladder and contribute to increased urgency and frequency.
2. BTL Emsella Treatment to Manage Frequent Urination
BTL Emsella Treatment is a revolutionary treatment that utilises electromagnetic energy to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles. This non-invasive procedure can significantly improve bladder control and reduce urinary frequency, particularly in those with overactive bladder symptoms.
BTL Emsella Treatment sessions typically last about 30 minutes and require no downtime, making it a convenient option for individuals seeking effective pelvic health solutions.
Tips and Techniques for Supporting Your Urinary Health
Taking proactive steps to maintain urinary health can significantly reduce the symptoms of frequent urination. Here are effective methods that can help manage fluid intake, improve bladder control, and support a healthier urinary system:
Tips on Managing Fluid Intake Wisely
1. Hydrate with Purpose
Maintaining adequate hydration is essential for urinary and overall health, but consider the timing and volume of intake. Spread water intake throughout the day rather than drinking large amounts at once, and reduce fluids in the evening to minimise nighttime urination.
2. Limit Bladder Irritants
Certain drinks—like caffeinated coffee, tea, and sodas, as well as alcohol—can irritate the bladder lining, triggering more frequent trips to the restroom. Try substituting with non-caffeinated herbal teas or water infused with cucumber or mint for a refreshing alternative that’s gentler on the bladder.
3. Moderate Intake of Acidic or Spicy Foods
Acidic foods (such as citrus fruits and tomatoes) and spicy meals can also irritate the bladder, potentially worsening symptoms of frequent urination. Experiment with cutting back on these items to see if it helps with bladder control.
Bladder Training and Control Techniques
1. Bladder Training
This technique involves gradually extending the time between bathroom trips to increase bladder capacity and retrain the bladder’s response to urgency. Start by setting a time interval (e.g., 30 minutes) between trips and gradually increase this interval as your bladder adapts. Keep a bladder diary to track progress and identify patterns in urinary frequency.
2. Timed Voiding
Planned voiding is another helpful approach, where you follow a scheduled bathroom routine instead of waiting for the urge to urinate. For instance, try going to the bathroom every two hours, even if you don’t feel the need, to help regulate the bladder’s cycle.
3. Practice Kegel Exercises
Strengthening pelvic floor muscles through Kegel exercises can help improve bladder control, particularly in cases of urge and stress incontinence. These exercises involve contracting the muscles that stop urine flow and holding the contraction for a few seconds, gradually increasing the duration and frequency over time.
Dietary Adjustments for Bladder Health
1. Incorporate Anti-inflammatory Foods
Foods high in antioxidants, such as berries, leafy greens, and nuts, may reduce inflammation, supporting bladder health and reducing irritation.
2. Optimise Fibre Intake
Constipation can increase pressure on the bladder, leading to more frequent urination. Eating a diet rich in fibre—from sources like whole grains, vegetables, and fruits—can support regular bowel movements, easing pressure on the urinary system.
Lifestyle Adjustments to Support Urinary Health
1. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Excess body weight puts pressure on the bladder, which can exacerbate urinary symptoms. Regular exercise and a balanced diet can help maintain a healthy weight, reducing strain on the pelvic floor.
2. Engage in Relaxation Practices
Stress and anxiety can worsen the sensation of needing to urinate frequently. Deep breathing exercises, mindfulness, and relaxation techniques like yoga can help manage stress, making it easier to maintain bladder control.
The Importance of Regular Check-Ups
Routine visits with a healthcare provider can help catch early signs of urinary health issues, enabling timely intervention. If symptoms like frequent urination or urinary leakage persist, or if new symptoms arise, speak openly with the doctor.
免費體驗
BTL Emsella Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
Your Urinary Health Starts From You!
Frequent urination is a challenge that can significantly impact one’s quality of life, but it is important to remember that help is available. Understanding the causes and symptoms of frequent urination, as well as exploring treatment options, is vital for effective management.
Seeking help from healthcare providers and considering innovative treatments like BTL Emsella Treatment can empower you to take control of their urinary health. Start addressing this issue openly, and you'll find the support and solutions needed to a fulfilling life without the burden of frequent urination.
BTL Emsella Treatment免費體驗
BTL Emsella Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
FAQ

1. What are the most common causes of pelvic organ prolapse, and how does it relate to frequent urination?
Pelvic organ prolapse occurs when weakened pelvic floor muscles allow organs, such as the bladder, to drop and press against the vaginal wall. This can increase the need for frequent urination due to pressure on the bladder. Ageing, childbirth, and chronic straining are common causes. Strengthening the pelvic floor through targeted exercises or considering supportive medical options can help relieve symptoms.
2. How does drinking too much fluid or certain beverages like alcohol and caffeine contribute to frequent urination?
Consuming too much fluid increases the volume of urine, which can lead to more frequent trips to the bathroom. Additionally, beverages like alcohol and caffeine are diuretics, meaning they stimulate the bladder to produce more urine. Avoiding or limiting these drinks, especially in the evening, can help reduce the need for urgent urination and improve bladder control.
3. What are other possible causes of frequent urination besides bladder infections?
While bladder infections are a common cause, other possible causes include pelvic organ prolapse, high fluid intake, and irritants like caffeine and alcohol. Pregnancy, especially in the second trimester, can also increase bladder pressure and the frequency of urination. Identifying the underlying cause can help guide effective treatment strategies.
4. Can pressure inside the lower abdomen from issues like constipation cause frequent urination?
Yes, pressure in the lower abdomen due to constipation or other conditions can place additional strain on the bladder, leading to an increased need to pass urine. Relieving abdominal pressure through diet, hydration, and exercise can help manage urinary symptoms and reduce discomfort.
5. What lifestyle adjustments can help manage the frequent need to pass urine without medical intervention?
Adjusting daily habits can reduce the urge to urinate frequently. Drinking smaller amounts of water throughout the day, rather than large amounts at once, can help regulate the need to urinate. Additionally, limiting alcohol and caffeine intake, especially before bed, can prevent unnecessary bladder stimulation. Maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in regular exercise also help alleviate pressure on the bladder, supporting overall urinary health.








