- Home
- Trend
- Weight Loss Strategies
- Acne Tips
- Hair Health Information
- Blemish Removal Tips
- Acne Scar Removal Tips
- Muscle Building Techniques
- Intimate Care Tips
- Postpartum Intimate Care
- Eye Bags Wiki
- Tips for Face Slimming
- Secret of Permanent Hair Removal
- Breast Enlargement Tips
- Cure to Snoring
- Marionette Lines
- Skin-Tightening Secrets
Hyperpigmentation can be triggered by skin inflammation, UV damage, or hormonal changes. According to dermatologists, dark spots, melasma, and pigmentation on the face or body can be lightened through six daily habits—learn them now!
What Causes Hyperpigmentation?

1. UV Damage
Melanin isn’t inherently bad—it’s produced by melanocytes in the skin's basal layer to protect against UV damage and sunburn. However, excessive sun exposure can cause an overproduction of melanin. If your skin’s metabolism is sluggish, melanin builds up and forms visible brown patches or sunspots. People with darker skin naturally have more melanin, which offers greater sun protection, making them less prone to sunburn.
2. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal imbalances—especially in women—can also cause pigmentation. During the 10 days around ovulation, levels of progesterone rise. Since the brain regulates both progesterone and melanin production through the same signaling pathway, this triggers heightened melanocyte activity. If metabolism is slow or UV protection is inadequate, excess melanin leads to visible pigmentation. Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, post-partum, or menopause also heighten the risk of melasma (also called hormonal spots).
3. Inflammation or Skin Injury
Pigmentation may occur after inflammation or skin trauma—such as acne, bug bites, cuts, or burns. Initially, red marks form as blood vessels dilate to bring healing agents to the injury. As skin heals, the area may still be inflamed and sensitive, triggering an increase in melanin to protect the skin. As a result, red scars may turn brown or black. This is why pigmentation often appears after scabs fall off.
Types of Hyperpigmentation
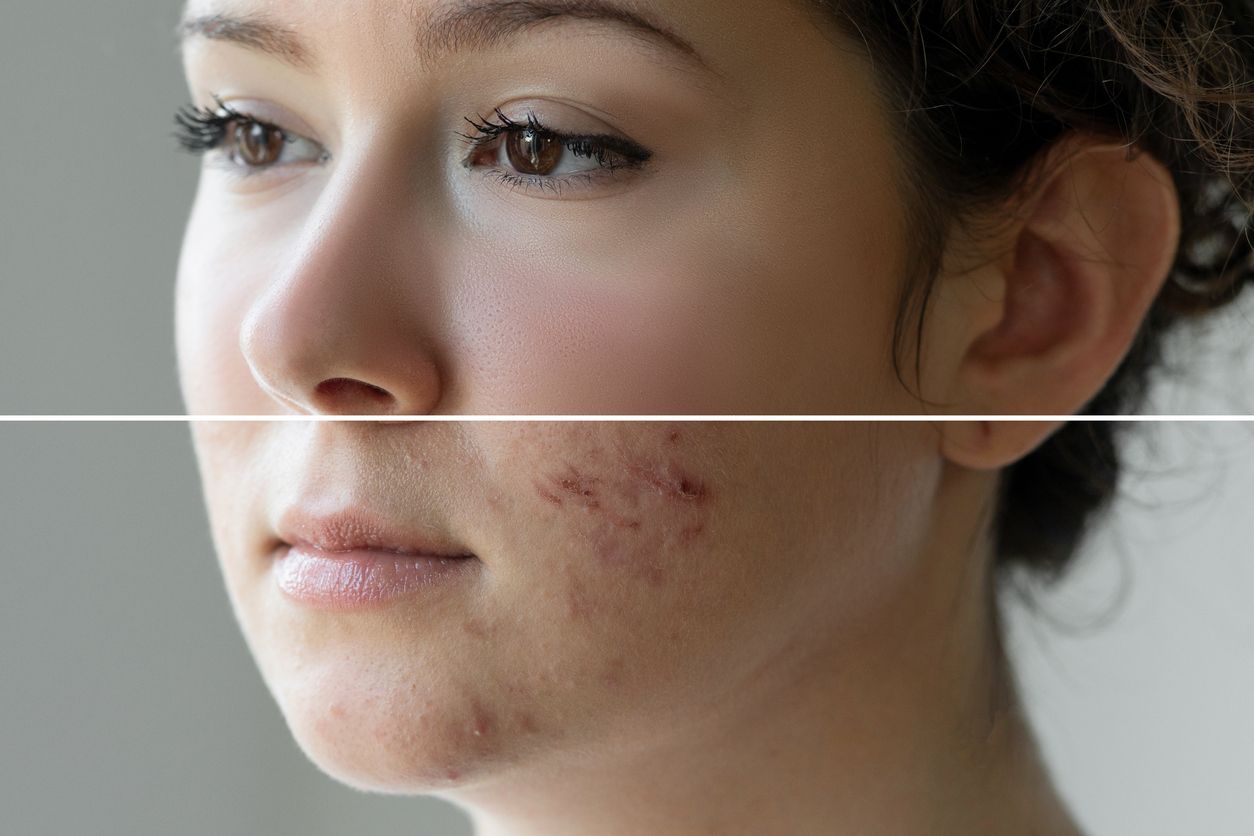
1. Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH)
Pigmentation after inflammation—like from eczema, injuries, acne, or insect bites—can appear red or brown. Red spots indicate ongoing inflammation or healing, while brown or black spots signal fully healed areas with melanin buildup. In real life, post-acne marks can look red, purple, dark brown, or even a mix of colors due to complex interactions between melanin, blood vessels, and scar tissue. PIH may also include indented (atrophic) or raised (hypertrophic) scars, each requiring different treatments.
2. Pigmented Spots: Melasma (Chloasma)
Pigmentation results from excessive melanin, which can be caused by hormone shifts, chronic sun exposure, heat, immune imbalance, slow metabolism, excess free radicals, or even stress and obesity. Among all types, melasma is the most stubborn to treat. That’s because melanin in melasma can exist across multiple skin layers and is often located near blood vessels. Treatments involving light or heat can worsen melanin production, leading to darkening or spread of the pigment.
3. Friction-Induced Pigmentation (e.g., Underarms)
Areas like underarms, knees, elbows, and heels can become darker—not from sun, but from frequent friction and skin thickening. Constant rubbing from movement or clothing leads to a buildup of keratin and melanin. In armpits, repeated arm movement and friction cause noticeable darkening and sometimes clogged hair follicles.
免費體驗
PicoCure Pigmentation Removal Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
How to Treat or Improve Hyperpigmentation
1. Whitening Creams for Targeted Pigmentation
Topical creams with active ingredients can help, depending on whether you're treating red or brown spots.
• For red PIH, use ingredients that calm inflammation and constrict blood vessels: olive leaf extract, green tea extract, azelaic acid, and niacinamide.
• For brown/black PIH, opt for: vitamin C, kojic acid, arbutin, AHAs, hydroquinone derivatives, retinoids, and tranexamic acid.
Apply morning and night directly on the affected area to prevent red marks from darkening and to speed up melanin breakdown.
2. The “Morning C, Night A” Routine
This trendy skincare method involves using vitamin C products in the morning to protect against free radicals and boost radiance, and vitamin A derivatives at night to encourage skin renewal, fight inflammation, and promote anti-aging. This combo helps combat UV damage throughout the day and supports overnight healing—making it an effective strategy to fade pigmentation.
3. Sun Protection Is Non-Negotiable
Aging is inevitable, and UV rays are one of nature’s strongest weapons. Every breath we take produces free radicals—and our DNA is attacked by them about 10,000 times daily. While our body can usually balance this, UV rays amplify the damage. They stimulate melanin production and lead to pigmentation and sunspots. To prevent this, consistent sun protection is a must.
4. Antioxidant-Rich Diet
Controlling melanin means strengthening your skin’s natural defenses and repairing cellular damage. Foods rich in antioxidants like vitamins A, B, C, and E, lycopene, carotenoids, polyphenols, anthocyanins, and flavonoids can help. Eat more leafy greens, citrus fruits, berries, fatty fish, seeds, and green tea to support metabolism and fight hyperpigmentation.
5. Chemical Peels (AHA Peels)
Our skin naturally sheds pigment over time, but this can take years—especially for deeper body pigmentation. Alpha-hydroxy acid (AHA) peels loosen the bonds between dead skin cells, making it easier to slough off melanin-heavy layers. These peels accelerate cell turnover and help fade spots, scars, and scabs more effectively.
6. Pico Laser Treatment for Pigmentation
When it comes to medical treatments, picosecond laser therapy is one of the most effective and fastest options to remove stubborn pigmentation.
Unlike older nanosecond lasers, pico lasers target melanin precisely and break it into ultra-fine particles. They use shorter light pulses with lower thermal damage, reducing the risk of rebound pigmentation and preventing worsening of melasma.
The shattered melanin is easier for the body to eliminate through metabolism. Just one treatment can show results for superficial spots—and repeated sessions can address deep, chronic pigmentation.
30-Minute Pigmentation Removal — PicoCure Pigmentation Removal Treatment
When melanin particles are too large, the skin can’t metabolize them effectively. The PicoCure Pigmentation Removal Treatment offered by Perfect Medical shatters these stubborn pigment clusters in just 30 minutes.
Using 4 wavelengths (1064nm, 650nm, 585nm, 532nm), the laser targets pigments in various skin layers, breaks them into dust-like particles, and helps the skin gradually eliminate them. Visible improvement can be seen after just one session—completely pain-free, non-invasive, and with no risk of rebound darkening.
What’s more, pico laser also stimulates collagen regeneration in the dermis. It replaces old, stiff collagen with new, youthful fibers, boosting hydration, firmness, and elasticity. Your skin will look visibly smoother and more radiant—like turning back the clock 10 years!
PicoCure is internationally recognized and trusted by thousands of satisfied users and influencers. Perfect Medical now offers a free trial of the treatment, including a complimentary professional skin analysis. Don’t miss this opportunity!
Get it Now: Perfect Medical PicoCure Pigmentation Removal Treatment免費體驗
PicoCure Pigmentation Removal Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
FAQ

Are fair-skinned people more prone to pigmentation?
People with darker skin naturally produce more melanin, making them less likely to burn. However, habits matter more than skin tone. Both fair and dark-skinned individuals can develop pigmentation—though it may be less visible on deeper complexions.
What causes hyperpigmentation?
Major causes include inflammation, UV damage, and hormones. Injuries trigger melanin production to protect healing skin. UV rays cause melanin to accumulate in deeper layers. Hormonal shifts—like during pregnancy or menopause—can also increase melanin and slow skin turnover, leading to pigmentation.
Why is melasma/hormonal pigmentation the hardest to treat?
Melasma (a.k.a. butterfly spots or chloasma) is challenging because melanin spreads across multiple skin layers and may connect to blood vessels. Treatments must be precisely targeted using advanced imaging and laser wavelengths. Incorrect treatment can worsen the pigmentation. Pico laser’s short pulse duration reduces heat damage and avoids triggering additional melanin, making it a safer option.
What are the treatment options for pigmentation?
Options include topical whitening creams (with vitamin C, kojic acid, tranexamic acid, etc.), the Morning C, Night A skincare approach, and clinical treatments like pico laser or AHA peels. Pico lasers shatter melanin for removal; AHA peels dissolve bonds between pigmented cells. Both promote collagen growth and improve overall skin quality.
How long does it take for scars and pigmentation to fade?
It depends on the depth and location. Facial pigmentation may fade in 3 months due to faster circulation. Body pigmentation can take 6 months or even years to lighten due to slower cell turnover. What’s visible on the surface may be just the tip of the iceberg.








