
- Home
- Trend
- Weight Loss Strategies
- Acne Tips
- Hair Health Information
- Blemish Removal Tips
- Acne Scar Removal Tips
- Muscle Building Techniques
- Intimate Care Tips
- Postpartum Intimate Care
- Eye Bags Wiki
- Tips for Face Slimming
- Secret of Permanent Hair Removal
- Breast Enlargement Tips
- Cure to Snoring
- Marionette Lines
- Skin-Tightening Secrets
That moment when a pimple finally heals should be celebratory—but for many, it's just the beginning of a longer battle. The dark spot left behind, known as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), often feels like a stubborn reminder of skin troubles past. Whether you're dealing with the aftermath of acne vulgaris, skin injury, or other inflammatory skin conditions, this comprehensive guide will arm you with cutting-edge solutions to fade those stubborn spots and prevent new ones from forming.
Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation: Why That Pimple Left a Dark Reminder
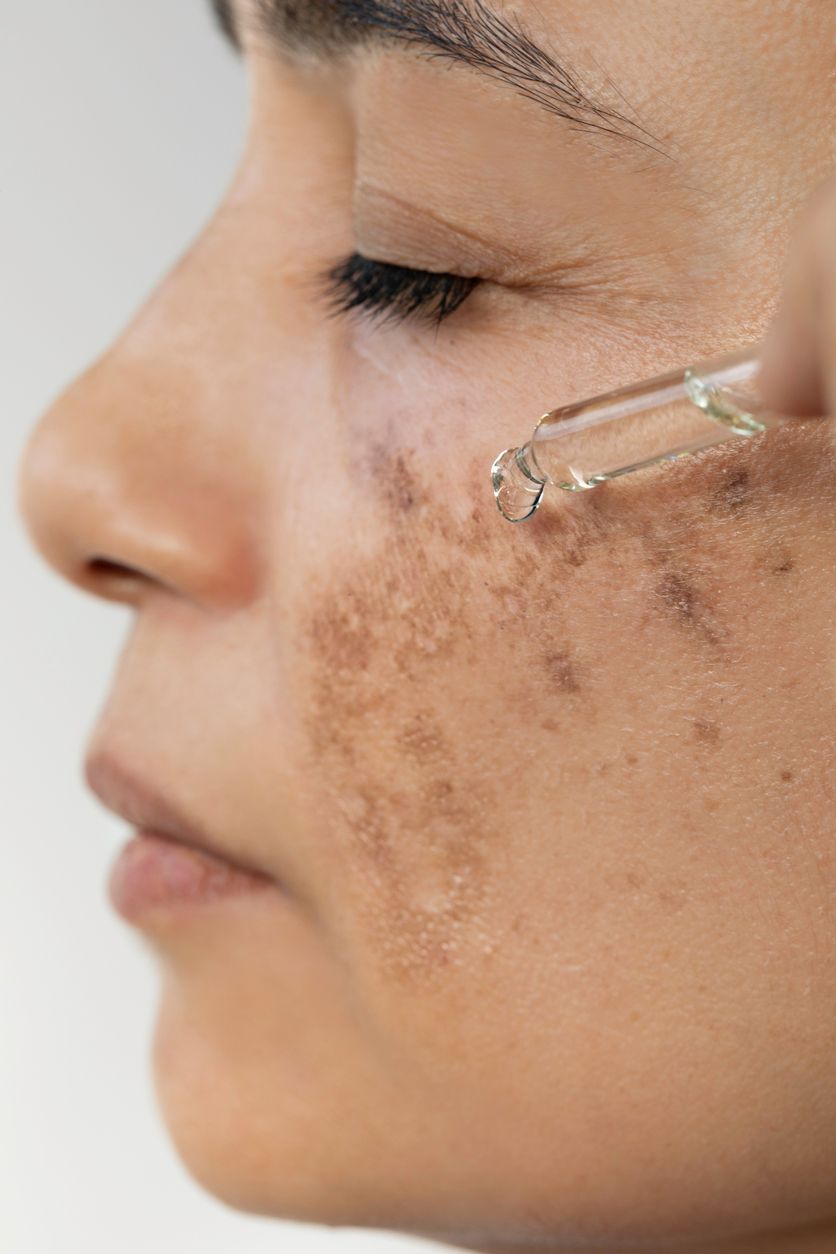
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation isn't just a simple dark spot—it's your skin's response to inflammation. When skin experiences trauma or inflammation, melanocytes (your pigment cells) go into overdrive, producing excess melanin as a protective response. This process, while natural, can lead to uneven skin tone that persists long after the initial inflammatory process has resolved.
For darker skinned individuals, this response tends to be more pronounced. Those with Fitzpatrick skin types III and above are particularly susceptible to PIH, often developing more intense hyperpigmented skin lesions that can take longer to fade. This isn't just about aesthetics—studies in skin therapy and pigment cell research show that PIH can significantly impact self-esteem and social interactions.
The Real Reason Some Spots Never Fade
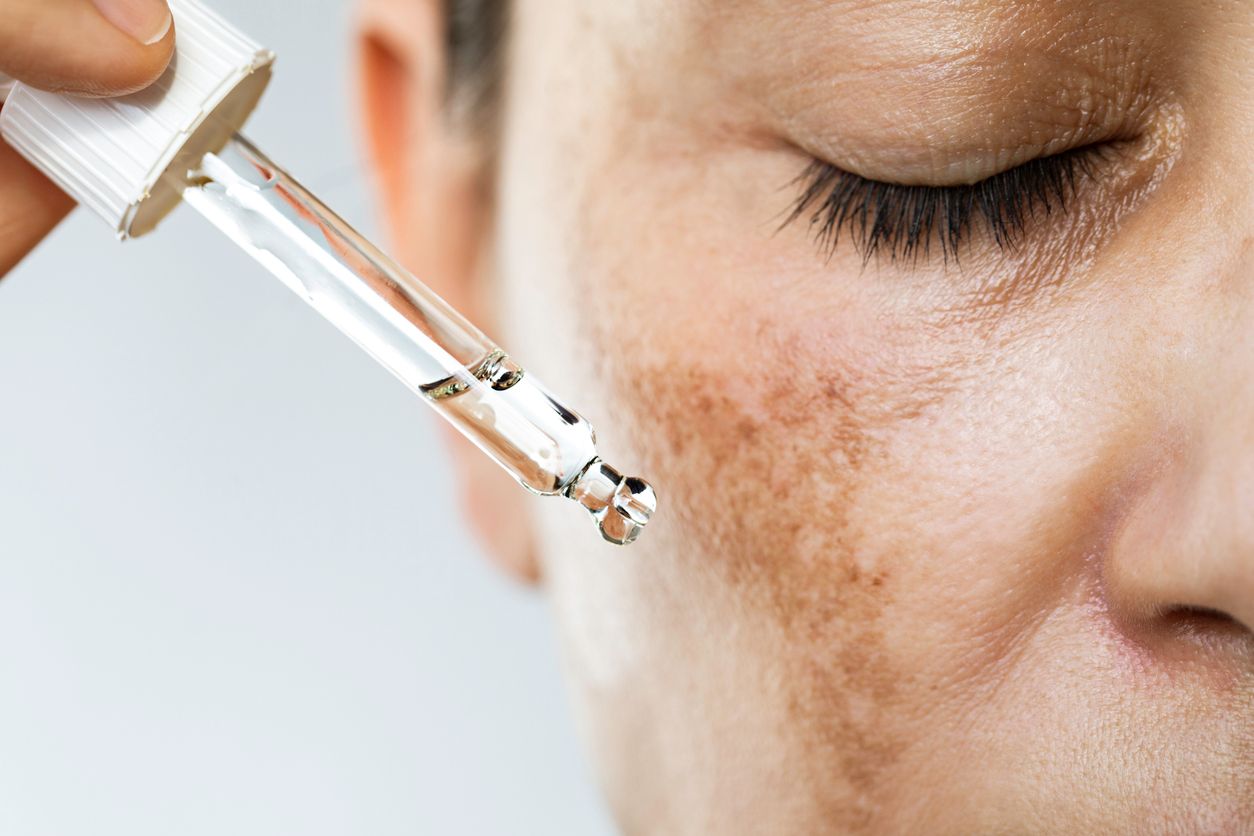
Understanding why certain dark spots seem resistant to fading involves delving into the two primary types of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH): epidermal PIH and dermal PIH. Each type has distinct characteristics that influence its appearance, treatment response, and longevity on the skin.
Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH)
PIH is a specific type of hyperpigmentation that occurs following inflammation or injury to the skin. It results from an overproduction of melanin in response to trauma, such as acne lesions, eczema flare-ups, or other skin irritations.
Causes: PIH can be triggered by various inflammatory conditions including acne, burns, psoriasis, and allergic reactions. It is particularly common in individuals with darker skin tones due to higher melanin content.
Appearance: PIH presents as flat patches of discoloration that can be brown, purple, or even blue-grey depending on the depth of pigmentation and the individual's skin tone. Unlike scars, PIH does not alter the texture of the skin.
Treatment: Treatment for PIH may involve topical agents like hydroquinone or retinoids, as well as procedures such as chemical peels or laser therapy for more stubborn cases. Sun protection is crucial since UV exposure can exacerbate pigmentation.
Epidermal Hyperpigmentation
Epidermal hyperpigmentation refers to increased melanin production confined to the epidermis, the outermost layer of skin. This condition typically manifests as flat, darkened patches or spots.
Causes: Common causes include sun exposure, hormonal changes (such as melasma), and skin injuries. Inflammatory responses can also lead to increased melanin production in the epidermis.
Appearance: The pigmentation appears as tan, brown, or dark brown spots that are generally flat and smooth, without any texture changes in the skin.
Treatment: Epidermal hyperpigmentation is often more responsive to topical treatments such as hydroquinone, retinoids, and chemical peels. These treatments aim to lighten the affected areas and promote an even skin tone.
Melasma
Melasma is a form of hyperpigmentation that typically appears as large patches on the face, often triggered by hormonal changes (e.g., pregnancy or birth control) and sun exposure.
Appearance: Melasma usually presents as symmetrical brown or grey-brown patches on sun-exposed areas like the cheeks and forehead.
Treatment: Similar to PIH, treatment may include topical lighteners, chemical peels, and sun protection. However, melasma can be more resistant to treatment than PIH.
Acne Scars
Acne scars are caused by damage to the skin from inflamed acne lesions. They result in permanent changes in skin texture.
Appearance: Unlike PIH, which is characterised by flat discoloration, acne scars can be either atrophic (depressed) or hypertrophic (raised), leading to uneven skin texture.
Treatment: Treatment options for acne scars include laser therapy, microneedling, and dermal fillers. These methods aim to improve skin texture rather than just reduce pigmentation.
Dermal Hyperpigmentation
Dermal hyperpigmentation occurs when excess melanin is deposited deeper in the dermis layer of the skin.
Appearance: This type of pigmentation may appear blue-grey and can be more challenging to treat compared to epidermal forms.
Treatment: Treatments may require more aggressive approaches such as stronger chemical peels or laser therapies due to the depth of pigmentation involved
免費體驗
PicoCure Pigmentation Removal Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
Most Important Thing You Should Start Doing: Preventing Sun Exposure
When it comes to managing post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), one of the most crucial steps you can take is to prevent sun exposure. Continuous exposure to sunlight not only darkens existing hyperpigmented areas but also plays a significant role in the formation of new spots. This issue is particularly relevant for individuals with darker skin tones, who may experience more pronounced changes in pigmentation due to increased melanin production triggered by sun exposure.
Importance of Broad-Spectrum Sunscreen
The application of broad-spectrum sunscreen should be viewed as an essential and non-negotiable aspect of your skincare routine, especially if you’re dealing with PIH. Broad-spectrum sunscreen protects against both UVA and UVB rays, both of which can exacerbate pigmentation issues.
UVB rays are primarily responsible for sunburn, while UVA rays penetrate the skin more deeply and contribute to skin ageing and pigmentation changes. By using a sunscreen that shields your skin from these harmful rays, you significantly reduce the risk of darkening existing spots and forming new ones.
• Daily Use: Regardless of the weather or season, daily application of sunscreen is vital. Even on cloudy days, up to 80% of UV rays can penetrate the clouds and reach your skin. Thus, applying sunscreen every morning, as part of your skincare regimen, helps maintain consistent protection.
• SPF Recommendations: Opt for a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30. Higher SPF formulations offer greater protection and are particularly beneficial for those with a history of PIH. For those with very fair skin or a higher risk of skin cancer, SPF 50 or above may be advisable.
• Reapplication: Sunscreen is not a one-time application; it should be reapplied every two hours, or more frequently if swimming or sweating. This ensures that your protection remains effective throughout the day, preventing any potential sun damage that could aggravate pigmentation concerns.
Promoting Fading of Dark Spots
Consistent use of sunscreen does more than just prevent new spots from forming; it also aids in the fading of existing dark spots, enhancing your overall skincare treatment efforts. When undergoing treatments for PIH—such as chemical peels, laser therapy, or topical treatments—your skin can become more sensitive and vulnerable to sun damage. Protecting your skin with sunscreen during these processes is essential for several reasons:
Support Treatment Efficacy: Sunscreen creates a protective barrier, allowing topical treatments to work more effectively without the interference of UV damage. When skin is shielded from sun exposure, treatments can penetrate better, leading to improved results in fading hyperpigmentation.
Minimising Inflammation: Sun exposure can trigger inflammation, which may worsen pigmentation issues. By preventing inflammation through sun protection, you help maintain a calm and balanced skin environment that is conducive to healing and reducing the appearance of dark spots.
Encouraging Skin Regeneration: With regular sunscreen use, the skin can regenerate more efficiently without the constant threat of sun damage. This regeneration is vital for skin health and can facilitate the natural fading of dark spots over time.
Technology Meets Transformation: The PicoCure Revolution
Although sunscreen is vital for safeguarding your skin and preventing additional hyperpigmentation, advanced technology plays a key role in improving outcomes and successfully minimising post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. PicoCure Pigmentation Removal Treatment from Perfect Medical is a groundbreaking solution for hyperpigmentation. This advanced technology uses four different wavelengths (1064nm, 650nm, 585nm, and 532nm) to target pigmentation at various depths in the skin, offering a versatility that traditional single-wavelength lasers can't provide.
Key Advantages
• Faster Treatment Times: Get effective results in less time.
• Precise Targeting: Focus on excess melanin with accuracy.
• Reduced Skin Irritation: Lower risk of discomfort during treatment.
• Versatile for Skin Types: Suitable for a variety of skin tones.
• Long-lasting Results: Enjoy improvements that last.
Breaking Down Pigment at Light Speed
The science behind PicoCure's effectiveness lies in its unique two-step approach. Nanosecond pulses are used to break down larger clusters of pigment, while picosecond pulses shatter the smaller remaining particles, making them easier to remove. This combination therapy is particularly effective in treating both epidermal and dermal post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), often achieving results where other treatments have failed.
Recommended Routine to Achieve Bright and Natural Skin Tone
To effectively manage and reduce post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), establishing a consistent skincare routine is essential. Here’s a simple, easy-to-follow guide that outlines your morning and evening skincare rituals, along with weekend treatments that can enhance your results.
Morning
Your morning skincare routine serves as the first line of defence against the formation of dark spots. Here’s how to set your day up for success:
1. Gentle Cleansing
Start with a non-irritating cleanser to avoid stripping your skin of essential moisture. Be sure to avoid harsh scrubbing, as this can irritate the skin and lead to more pigmentation issues.
After cleansing, pat your face dry gently with a soft towel.
2. Active Ingredients
Azelaic Acid Cream (15-20%): This ingredient helps reduce inflammation and pigmentation.
Vitamin C Serum: A powerful antioxidant that brightens the skin and protects against sun damage.
Kojic Acid Products: These help inhibit melanin production, further assisting in lightening dark spots.
3. Sun Protection
Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher to shield your skin from harmful UV rays. Consider wearing protective clothing, like hats or long sleeves, to further minimise sun exposure.
Remember to reapply your sunscreen every two hours, especially if you’re spending time outdoors.
Evening
At night, your skin is busy repairing itself, making this the perfect time to use targeted treatments:
1. Treatment Products
Topical Retinoids: These help accelerate cell turnover, improving the texture and tone of your skin.
Glycolic Acid: Start with lower concentrations and gradually increase as your skin tolerates it. This ingredient gently exfoliates, promoting new cell growth.
Azelaic Acid: Use again at night to further reduce pigmentation and prevent breakouts.
2. Hydration
Choose non-comedogenic moisturisers that won’t clog your pores while providing hydration.
Look for products with healing ingredients, like ceramides or hyaluronic acid, to restore the skin’s moisture barrier.
Incorporate barrier repair products that help strengthen the skin’s natural defences against environmental stressors.
Weekend Warriors
Professional treatments can provide a significant boost to your skincare routine, helping to expedite the fading of PIH:
1. PicoCure Sessions
Schedule these treatments every 4-6 weeks for optimal results. These sessions use customised wavelength combinations tailored to your specific skin needs. Expect progressive improvements in skin tone and texture with each session.
2. Supporting Treatments
Chemical Peels: These help exfoliate the outer layer of skin, revealing brighter skin underneath and reducing pigmentation.
LED Therapy: This non-invasive treatment promotes healing and can help reduce inflammation and pigmentation.
Specialised Facials: Look for facials that focus on brightening and exfoliating to further enhance your routine.
免費體驗
PicoCure Pigmentation Removal Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
The Path Forward
Treating post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation requires patience, consistency, and the right combination of treatments. While PIH can be stubborn, understanding your skin's needs and using advanced treatments like PicoCure, combined with proper skincare and sun protection, can lead to significant improvement.
With the right approach and modern treatments like PicoCure, those stubborn spots don't stand a chance. Your journey to clearer, more even-toned skin starts with understanding PIH and taking action with proven solutions.
免費體驗
PicoCure Pigmentation Removal Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
FAQ

1. I've heard darker skin types are more prone to PIH after acne. Why is this, and what precautions should I take?
The pathophysiology of postinflammatory hyperpigmentation is indeed more complex in dark skinned patients. This is because melanin pigment production is naturally more active in these skin types, especially in Fitzpatrick skin types III and above. When inflammation occurs from post acne marks or other skin conditions, the melanocytes in the papillary dermis become hyperactive.
2. What's the difference between epidermal and dermal PIH, and how does this affect treatment?
Epidermal postinflammatory hyperpigmentation occurs in the upper skin cells and appears light brown, while dermal melanosis occurs deeper in the surrounding skin and appears darker. This distinction is crucial for treatment planning because epidermal PIH typically responds better to topical treatment options, whereas dermal PIH may require more aggressive approaches. The depth of the underlying post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation directly influences both treatment choice and duration.
3. Can conditions like atopic dermatitis and systemic lupus erythematosus cause PIH? How is treatment different?
Yes, inflammatory conditions including atopic dermatitis, lichen planus, and systemic lupus erythematosus can indeed trigger facial hyperpigmentation. The approach to treating hyperpigmentation from these conditions requires special consideration because the underlying condition must be addressed first before targeting the PIH. Treatment typically involves carefully selected topical medications and regular skin therapy monitoring.
4. What's the most effective topical regimen for treating PIH?
According to research in skin therapy lett, the most effective approach combines several key ingredients working in synergy. A comprehensive regimen typically includes topical tretinoin for cell turnover, salicylic acid for gentle exfoliation, and products containing epidermal growth factor. Sun protection factor products play a crucial role and should be used consistently.
5. How do clinical features of PIH differ between lighter skin and darker skin types?
The clinical features of pigmentation disorders show marked differences between skin types. In lighter skin colour, PIH typically appears light brown and often resolves faster with standard topical treatments. However, in darker skin types, the pigmentation tends to be more intense, with a higher risk of dermal melanosis and generally requires a longer treatment duration. Darker skin types often need specialised cosmetic procedures and more aggressive sun protection measures.








