- Home
- Trend
- Weight Loss Strategies
- Acne Tips
- Hair Health Information
- Blemish Removal Tips
- Acne Scar Removal Tips
- Muscle Building Techniques
- Intimate Care Tips
- Postpartum Intimate Care
- Eye Bags Wiki
- Tips for Face Slimming
- Secret of Permanent Hair Removal
- Breast Enlargement Tips
- Cure to Snoring
- Marionette Lines
- Skin-Tightening Secrets
Acne is like an upgraded version of pimples—bigger, more uncomfortable, and slower to heal! It forms when the hair follicles and surrounding skin cells react to infection and inflammation. Severe acne not only affects your skin quality but can also block follicles and disrupt facial circulation, signaling a decline in your body’s metabolic function. Let’s break down the 7 major causes of acne for your acne health, and explore the most comprehensive treatment solutions. Don’t want to see a dermatologist? Stay tuned—there’s a surprise at the end that’s sure to satisfy!
Know Your Enemy to Defeat It: 7 Major Acne Triggers
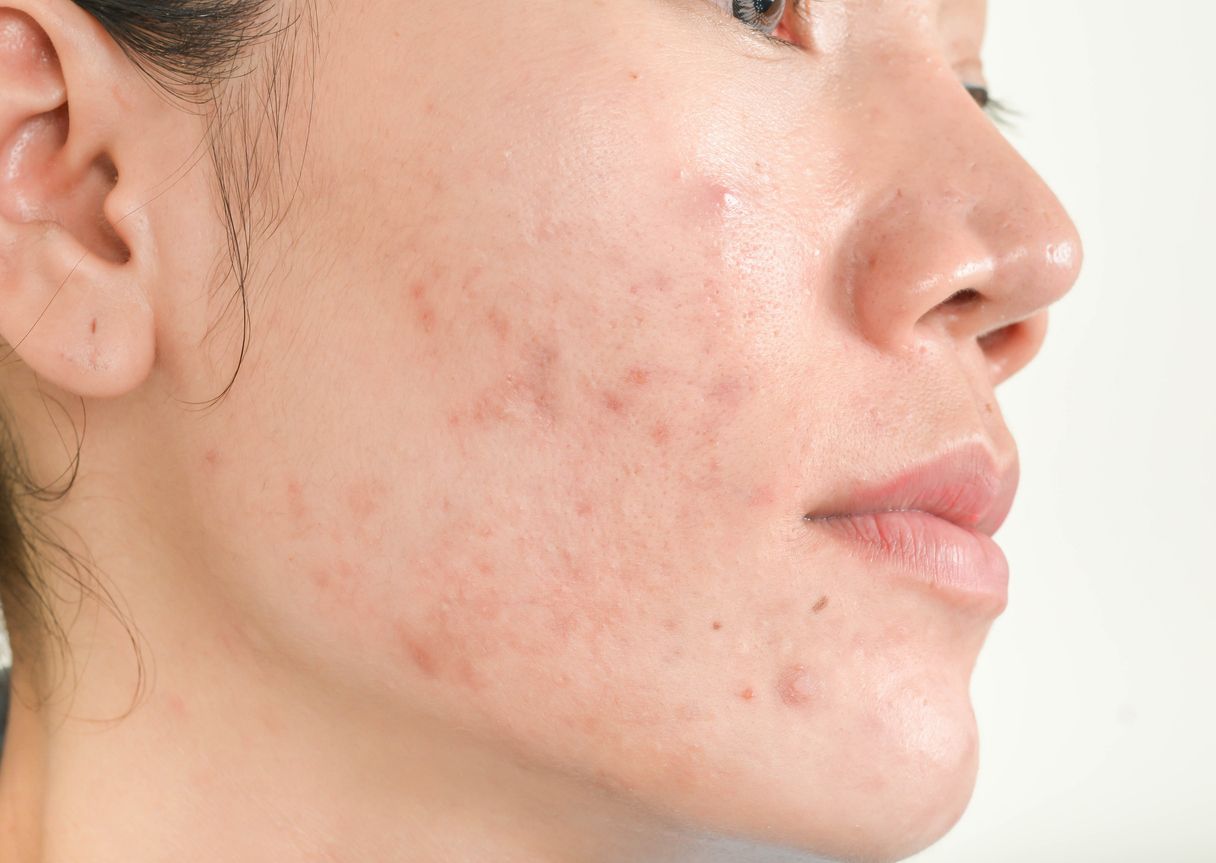
1. Buildup of Keratin Leads to Blocked Pores
Overactive sebaceous glands are a major culprit behind acne, especially during puberty or under the influence of androgens. Excess sebum clogs pores and feeds bacteria. The first step of acne formation usually starts with "follicular hyperkeratinization"—when dead skin cells accumulate at the pore opening, sebum gets trapped, forming comedones (blackheads and whiteheads), which are ideal breeding grounds for acne.
2. Bacterial Infection Worsens Acne
Cutibacterium acnes, a common anaerobic bacterium in hair follicles, thrives in clogged, oily environments. It breaks down sebum and produces fatty acids that irritate the skin, leading to redness, swelling, and inflammation—key features of pustular acne.
3. Inflammation Causes Redness and Pain
When your immune system detects bacteria or irritants, it triggers inflammation. That’s why acne often appears red, swollen, and painful. Persistent inflammation can lead to acne scars and long-term skin concerns.
4. Hormonal Imbalances Disrupt Sebum Production
Hormonal fluctuations are a major internal cause of acne. Puberty, menstrual cycles, pregnancy, or conditions like PCOS (polycystic ovary syndrome) can all increase sebum production, causing recurring breakouts.
5. Diet Directly Affects Skin Health
Studies suggest that excessive intake of sugar, oily foods, and dairy may contribute to acne. These can raise insulin and IGF-1 levels, which indirectly stimulate sebum production and keratin buildup. So, diet control is key in managing acne.
6. Irregular Sleep Worsens Acne
Lack of sleep or staying up late disrupts hormonal balance and impairs skin repair, causing abnormal oil secretion and worsening acne. A consistent sleep schedule can help regulate hormones and boost your skin’s recovery.
7. Stress Negatively Impacts Skin
Stress increases cortisol (the stress hormone) and androgens, both of which boost sebum production and clog pores. It also weakens the skin’s self-healing abilities, making acne harder to clear and more likely to become chronic.
6 Types of Acne: It’s Not Just Teen Pimples!
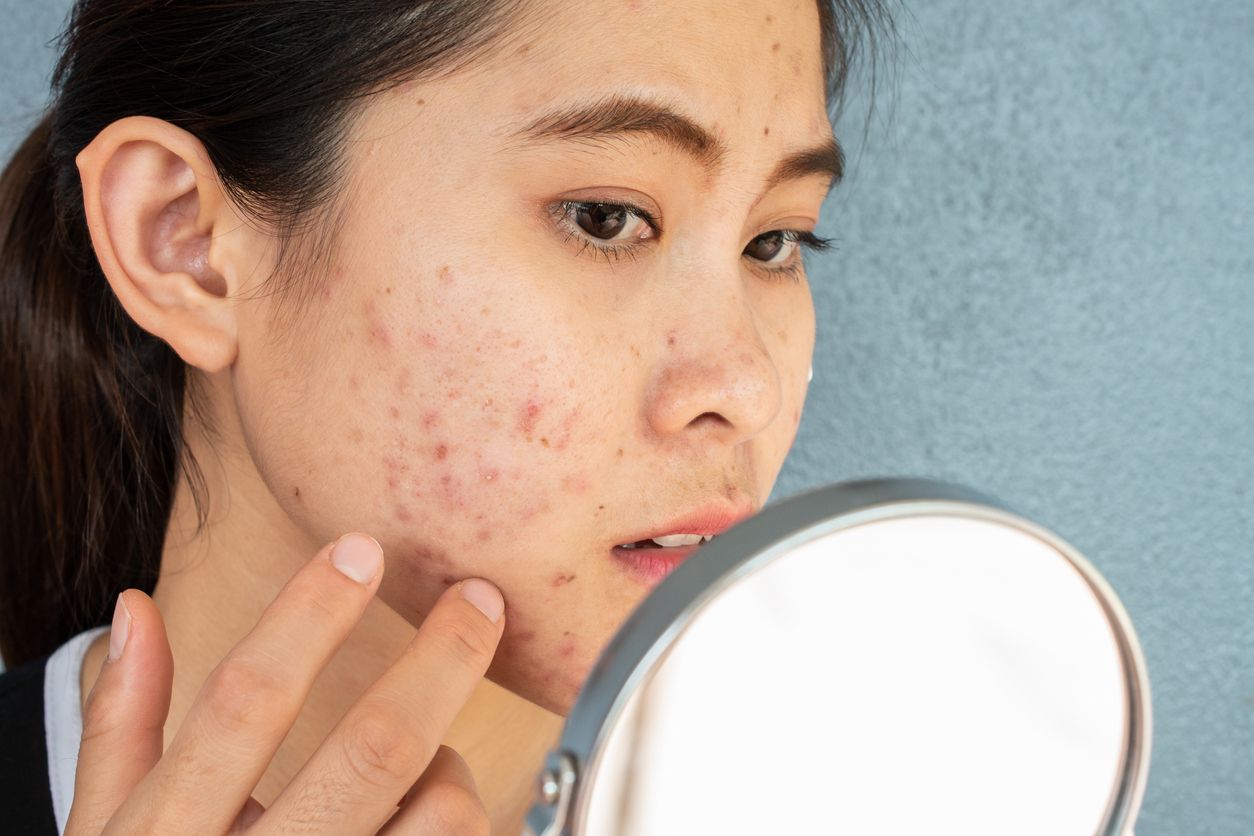

1. Blackheads: Open Comedones
Blackheads are early signs of acne and are considered open comedones. When pores stay open, sebum and keratin are exposed to air, oxidize, and turn black. Though not inflamed, poor hygiene can lead to inflammatory acne.
2. Whiteheads: Closed and Hidden Risks
Whiteheads are closed comedones—small, skin-colored or white bumps caused by completely blocked follicles. While less noticeable initially, they can turn into inflamed pimples if oil production increases or bacteria get involved.
3. Papules: Early Inflammatory Acne
When comedones become infected, small red bumps or papules form. These are inflamed lesions that may be mildly painful and are the immune system’s response to bacterial activity. Improper handling can cause scarring.
4. Pustules: Swollen Acne with Pus
Pustules are more inflamed than papules, often appearing red with a white pus-filled center. These result from a strong immune reaction and bacterial activity. Squeezing them can damage the skin and lead to pigmentation or pits.
5. Cystic Acne: Deep and Severe
Cystic acne forms when sebum and dead skin combine deep within the skin. These swollen, painful bumps may form pus-filled sacs. Due to intense inflammation, they’re hard to heal on their own and may leave permanent scars—medical treatment is strongly advised.
6. Nodular Acne: Hard and Long-Lasting
Similar to cysts, nodules are deep, hard, and painful but without pus heads. They take longer to heal and are common in men or those with hormonal imbalances. Treatment often requires oral medication and medical intervention.
免費體驗
Acne Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
The Best Acne-Busting Plan: Tailored Care by Acne Type
1. Comedonal Acne (Blackheads and Whiteheads)
• Cleansing: Use a gentle, non-irritating face wash twice daily. Avoid over-washing to protect the skin barrier.
• Exfoliation: Apply salicylic acid or AHA-based exfoliants 1–2 times a week to help clear pores.
• Product Tips: Look for serums or lotions containing salicylic acid, AHAs, or retinol.
2. Inflammatory Acne (Papules and Pustules)
• Anti-Inflammatory Care: Use products with tea tree oil, centella asiatica, or aloe vera to soothe skin.
• No Squeezing: Popping pimples can worsen inflammation or cause scarring.
• Product Tips: Try creams or gels with benzoyl peroxide or azelaic acid for antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects.
3. Cystic/Nodular Acne
Severe acne should be treated by a dermatologist.
• Oral Medication: Doctors may prescribe antibiotics or isotretinoin to reduce inflammation and oil production.
• Corticosteroid Injections: Injecting steroids directly into cysts or nodules can quickly reduce inflammation and shrink acne.
Build an Acne-Resistant Routine: When to See a Dermatologist
1. Choose the Right Skincare Regimen
• Know Your Skin Type: Whether oily, dry, combination, or sensitive—choose appropriate cleansers, moisturizers, and sunscreens.
• Gentle Cleansing: Avoid harsh face washes that strip your skin.
• Hydrate Properly: Use moisturizers to balance oil and water levels.
2. Maintain Healthy Lifestyle Habits
• Balanced Diet: Reduce intake of sugar, fat, and dairy. Eat more fruits and vegetables.
• Regular Sleep: Avoid staying up late. Aim for adequate rest.
• Manage Stress: Try exercise, meditation, or yoga to relieve stress.
3. Smart Makeup Habits
• Non-Comedogenic Products: Choose makeup labeled "non-comedogenic" or "won’t clog pores."
• Thorough Cleansing: Always remove makeup completely before bed.
• Limit Wear Time: Give your skin time to breathe by going makeup-free when possible.
When to See a Dermatologist:
• Over-the-counter products aren’t helping
• You have cystic or nodular acne
• Acne is affecting your quality of life or confidence
• Drugstore solutions don’t deliver noticeable results
The Ultimate Acne Therapy: Perfect Medical’s Acne Treatment
Complete skin renewal in just one relaxing session—say goodbye to oily, acne-prone skin!
No matter how severe your acne is, Perfect Medical’s Acne Treatment is here to help! This targeted therapy addresses acne, acne scars, blackheads, whiteheads, enlarged pores, dehydration, and dullness. Even painful, pus-filled pimples can be effectively treated, helping your skin return to a healthy, stable state.
With years of experience in Hong Kong’s beauty scene, Perfect Medical uses patented dual-spiral vacuum extraction + gentle dermabrasion technology. It softens and removes dead skin, clears follicles, balances oil production, and infuses purifying ingredients deep into the skin to stimulate collagen regeneration and activate skin cell renewal. The result? Lasting oil control and clearer, acne-free skin.
Try it now and enjoy: Professional Skin Analysis + Perfect Medical Acne Treatment!
Book Your Acne Treatment Now免費體驗
Acne Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
FAQ

Why is sebum linked to acne?
Most acne forms when overactive sebaceous glands produce too much oil, which mixes with dead skin and bacteria, causing inflammation.
Are blackheads and pimples considered acne?
Yes. Acne is a more severe, progressed form of blackheads and pimples—harder to treat and longer to heal.
Can oral antibiotics cure acne?
Yes, moderate to severe acne may improve with oral antibiotics.
What topical treatments are good for acne?
Mild acne can be treated with ointments containing salicylic acid or benzoyl peroxide. For more serious cases, consult a doctor.
Can stress cause acne?
Yes. Stress can disrupt hormone levels and increase the chance of breakouts.








